Test: Spirometry, DLco, Alveolar-Arteriolar Gradient & Types of Respiratory Failure- 1 - NEET PG MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Spirometry, DLco, Alveolar-Arteriolar Gradient & Types of Respiratory Failure- 1
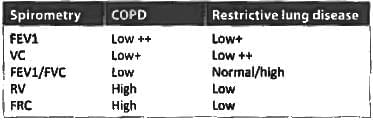
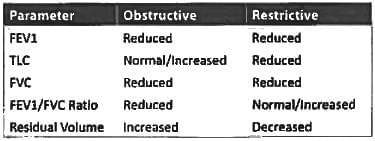
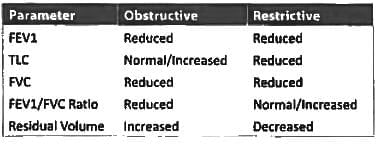
Which of these is false regarding restrictive lung disease? (JIPMER May 2018)
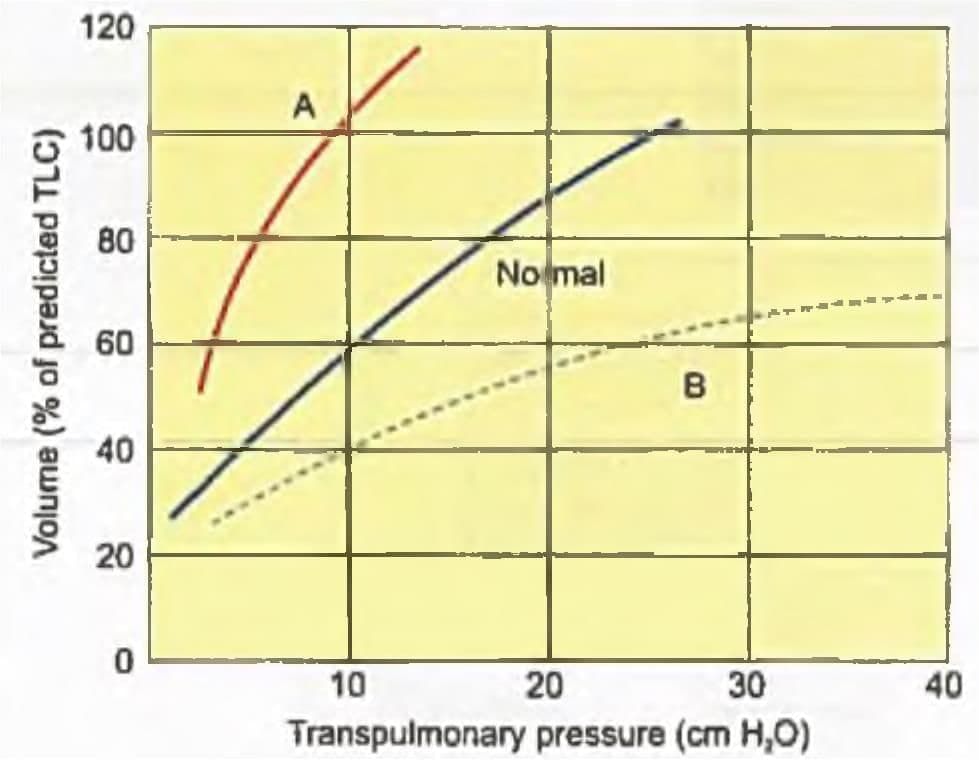
Curve A signifies which of the following? (AIIMS Nov 2018)

Which is the best test to differentiate between central and pulmonary cause of hypoventilation? (Recent Pattern Questions)
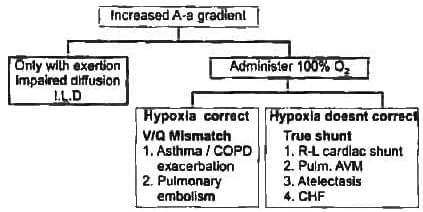
Which of the following will have the highest magnitude of increased Alveolar arteriolar gradient?
What will be the effect on spirometry in case of lobectomy done in case of bronchogenic carcinoma? (JIPMER May 2015)
A man working in a coal mining factory for 16 years develops symptoms of progressively worsening breathlessness and cough with expectorations a spirometry was performed and his values were as follows FEV 1 - 1.4 I/min FVC 2.8 I/min and with FEV1/FVC ratio of 50. What could be the cause? (UPSC CMS 2015)
The diffusion capacity of lung is decreased in all of the following conditions except: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
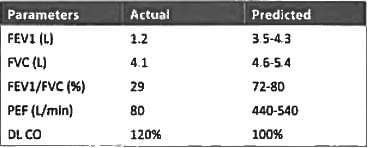
The results of the pulmonary functions tests shown below, the best diagnosis is: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
A factory worker was found unresponsive in his workplace. He is afebrile anicteric, tachypneic drowsy pale discoloration with clear lung field and hyperdynamic cardiovascular findings. His ABG with 100% oxygen after intubation was
pH = 7.45
pO₂ = 80 mm Hg
pCO₂ = 30 mm Hg
SaO₂ = 95%
What is the most likely diagnosis? (UPSC CMS 2014)
All show increased alveolar-arterial O₂ gradient except? (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
A patient with blood chemistry of pH 7.3, CO₂ of 60 and HCO₃ of 28 mEq/dl are indicative of: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
A patient presents with breathlessness. He has bilateral basal crepitations, lung function tests reveal decrease in total lung capacity (TLC) and vital capacity (VC) with normal FEV1/VC ratio. The most likely diagnosis is: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Which of the following is not true in obstructive lung disease? (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Residual volume is best measured by? (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
In restrictive lung disease: (AIPG2010)
If FEV1 is 1.3 L, FVC is 3.1 L in an adult man, the pattern is suggestive of: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Alveolar-arterial tension gradient increases in all except: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Following pulmonary changes are seen in restrictive lung disease except: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)