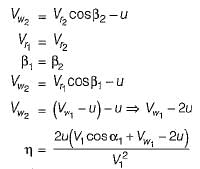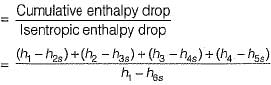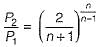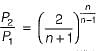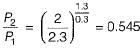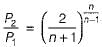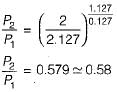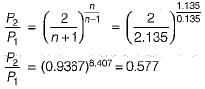Test: Steam Turbines - 3 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Steam Turbines - 3
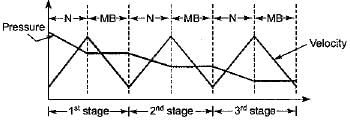
What changes occur in pressure and velocity when steam flows through the second row of moving blades of a velocity compounded impulse turbine?
What changes occur in the magnitude of pressure and velocity when steam flows through the nozzles of second stage of pressure compounded impulse turbine?
The expansion of steam, as it flow over the blade of reaction turbine approximated as
A Curtis stage, Rateau stage and a 50% reaction stage in a steam turbine are examples of
The correct sequence of the given steam turbines in the ascending order of efficiency at their design points is
Which one of the following relationship between angles of fixed blades and moving blades corresponds to that of parson’s turbine
In Parson’s reaction turbine the relative velocity at outlet as compared to inlet is
In an impulse turbine, the energy supplied to blade per kg of steam is equal to
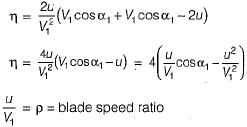
In Parson’s turbine if α is nozzle angle, then what is the maximum efficiency of the turbine
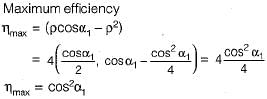
Maximum efficiency of a De-Laval turbine is
where α = Nozzle angle
Given
Vb = Blade speed
V = Absolute velocity of steam entering the blade
α = Nozzle angle
The efficiency of an impulse turbine is maximum when
In which one of the following steam turbines, steam is taken from various points along the turbine, solely for feed-water heating?
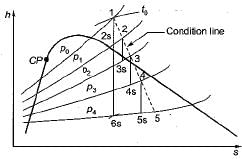
The reheat factor for steam turbines is defined as ratio of
What is the value of the reheat factor in multistage turbine?
Which of the following method is/are adopted to bring down the speed of an impulse turbine to practical limits?
1. Use of flywheels
2. Use of governor
3. Compounding
4. Increasing the load
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
At which location of a converging-diverging nozzle, does the shock-boundary layer interaction take place
The variation of flow through a convergent- divergent nozzle with variation in exit pressure is represented as
The critical pressure ratio for maximum discharge through a nozzle is given by
The value of critical pressure ratio for superheated steam is
The value of critical pressure ratio for initially wet steam is
The value of critical pressure ratio for initially dry saturated steam is
For critical pressure ratio, what is the discharge through a nozzle?


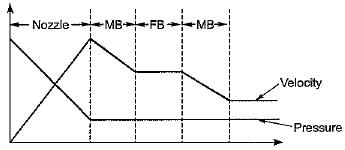


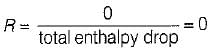
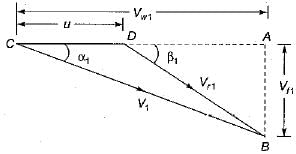
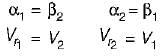
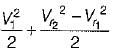
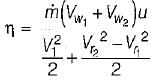
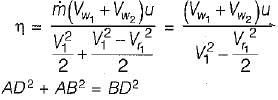
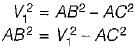
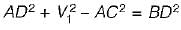
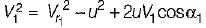
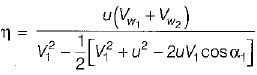

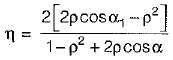
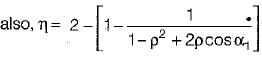
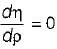
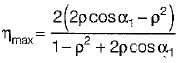
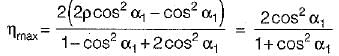
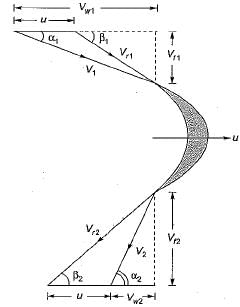
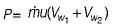

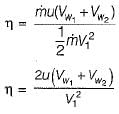
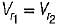 and blade is symmetrical i.e., β1 = β2 from the velocity triangle
and blade is symmetrical i.e., β1 = β2 from the velocity triangle