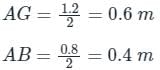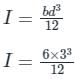Test: Submerged Bodies - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Fluid Mechanics for Civil Engineering - Test: Submerged Bodies
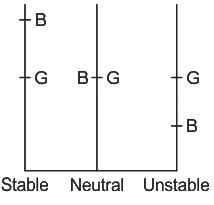
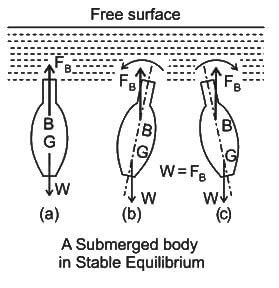
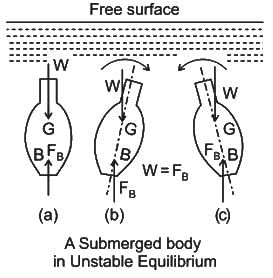
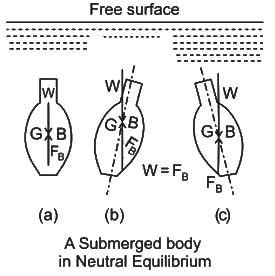
For a neutrally immersed buoyant body, G and B represent the centre of gravity and centre of buoyancy. Which of the following statements is/are INCORRECT?
(i) If G is directly below the B of the body, then the body is in stable state.
(ii) If G is directly above B, the body is in unstable state.
(iii) If G and B are coincident, the body is in neutrally stable state.
(iv) If G is not aligned vertically with B, the body must require disturbance force to attain a stable state.
(i) If G is directly below the B of the body, then the body is in stable state.
(ii) If G is directly above B, the body is in unstable state.
(iii) If G and B are coincident, the body is in neutrally stable state.
(iv) If G is not aligned vertically with B, the body must require disturbance force to attain a stable state.
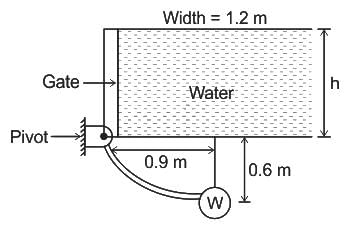
The massless, 1.2 m wide gate shown in fig is pivoted about the frictionless hinge and is held in place by 8896 N counterweight W, Determine the water depth h ______ (m).

A floating body attains stable equilibrium if its metacenter is
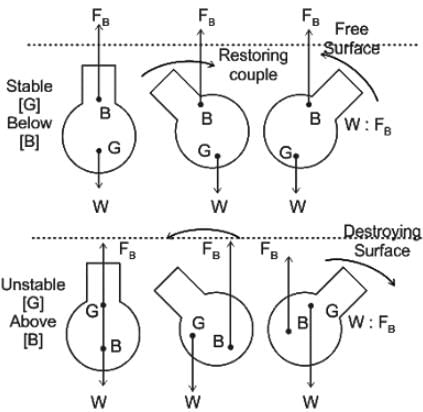
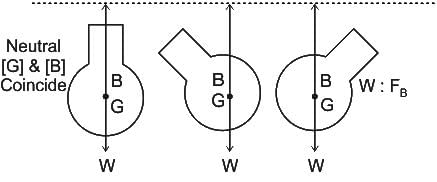
For a completely submerged body with centre of gravity ‘G’ and centre of buoyancy ‘B’, the condition of stability will be
For the rotational stability of a completely submerged body
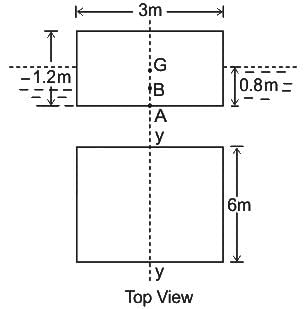
A rectangular block (6m × 3m × 1.2m) is immersed in sea water with depth of immersion 0.8m in water. If the centre of gravity is 0.6 m above the bottom of the block, determine the metacentric height. The density for sea water = 1025 kg/m3
A solid cylinder of 15 cm diameter and 40 cm long, consists of two parts made of different materials. The first part at the base is 1.5 cm long and of specific gravity = 6.5. The other part of the cylinder is made of the material having specific gravity 0.75. State, if the it can float vertically in water.
When body is completely or partially immersed in a fluid, how much its weight be distributed for it to be in stable equilibrium.
|
54 videos|97 docs|110 tests
|