Test: Theory Of Cost- 2 - CA Foundation MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Business Economics for CA Foundation - Test: Theory Of Cost- 2
If total cost at 10 units is Rs. 600 and Rs. 640 for 11th unit. The marginal cost of 11th unit is:
At which point does the marginal cost curve intersect the average variable cost curve and short run average total cost curve?
What is the total cost of production of 20 units, if fixed cost is Rs. 5,000 and variable cost is Rs. 2/-?
A firm’s average fixed cost is Rs. 40 at 12 units. What will be the average fixed cost at 8 units:
A firm producing 7 units of output has an average total cost of Rs. 150 and has to pay Rs. 350 to its fixed factors of production. How much of the average total cost is made up of variable cost ?
The Average fixed cost for producing on output of 6 units of a product by a firm is Rs. 30. The same cost for producing an output of 4 units will be Rs. ______.
With fixed cost of Rs. 400, a firm has an average total cost of Rs. 3 and an average variable cost of Rs. 2.50. Its output is _________.
Which of the following curves never touch any axis but is downward?
Suppose the total cost production of a commodity ‘x’ is Rs. 1, 25,000 out of which Implicit cost is Rs. 35,000 and normal profit is Rs. 25,000. What would be the explicit cost of commodity x?
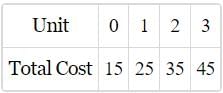
What will be the AFC of 3 units of Output as per table given below?
The total cost of production of 10 units is Rs. 200. When production is increased to 20 units its total cost becomes Rs. 600. What will be its marginal cost.
From the following details, firm out the average variable cost of 10 units:
OUTPUT : 0 10 20
Total cost : Rs. 200 Rs. 400 Rs. 800
A forms AFC is Rs. 200 at 10 units of output what will be it at 20 units of output?
If the LAC curve falls as output expands, this is due to ______________________.
Payment made to outsiders for their goods and services are called :
|
86 videos|255 docs|58 tests
|