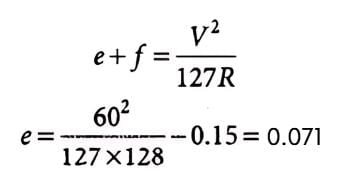Test: Transportation Engineering- 1 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Transportation Engineering- 1
If the load, warping and frictional stresses in a cement concrete slab are 210 N/mm2 , 90 N/mm2 and 10N/mm2 respectively. The critical combination of stresses during summer mid-day is
The superelevation needed for a vehicle travelling at a speed of 60 km/h on a curve of radius 128 m a surface with a coefficient of friction of 0.15 is
The maximum super elevation to be provided on a road curve is 1 in 15. If the rate of change of super elevation is specified as 1 in 120 and the road width is 10m, then the minimum length of the transition curve on the either end will be
In highway geometric design, once the cumulative speed distribution is drawn, the design adequacy is checked at
Penetration to know the grade of bitumen is measured in
For total reaction time of 2.5 s, coefficient of friction 0.35, and design speed of 80 km/h, what is the stopping sight distance on a highway?
What is the superelevation for a horizontal highway curve of radius 500 m and speed 100 km/h in mixed traffic condition?
The length of a transition curve for a circulation curve of radius 300 m and for a design speed of 15 m/s, when the rate of change of centrifugal acceleration is 0.3 m/s3 is
Bitumen grade 80/100 indicates that under the standard test conditions, penetration value of bitumen would vary from
Modulus of subgrade reaction using 30 cm diameter plate is obtained as 200 N/cm3. The value of the same (in N/cm3) using the standard plate will be __________ N/cm3.
A rest vertical curve joints two gradients of +3% and –2% for a design speed of 80 km/h and the corresponding stopping sight distance of 120 m. The height of driver’s eye and the object above the road surface are 1.20 m and 0.15 m, respectively. The curve length (which is less than stopping sight distance) to be provided is _________ m.
The design speed for a two-lane road is 80 km/h. When a design vehicle with a wheel base of 6.6 m is negotiating a horizontal curve on that road, the off-tracking is measured as 0.096 m, the required widening of carriageway of the two-lane road on the curve is approximately
It is proposed to widen and strengthen an existing two lane NH section as a divided highway. The existing traffic in one direction is 2500 commercial vehicles (CV) per day. The construction will take 1 yr.
The design CBR of soil subgrade is found to be 5% Given: Traffic growth rate for CV = 8% Vehicle damage factor = 3.5 (standard axles per CV) Design life = 10 yr, Traffic distribution factor = 0.75
The cumulative standard axles 9 (msa) computed are
The width of the expansion joint is 20 mm in a cement concrete pavement. The laying temperature is 20° C and the maximum slab temperature in summer is 60° C. The coefficient of thermal expansion of concrete is and the joint filler compresses upto 50% of the thickness. The spacing between expansion joints should be
A vehicle moving at 60 km/h on an ascending gradient of a highway has to come to stop position to avoid collision with a stationary object. The ratio of lag to brake distance is 6:5. Considering total reaction time of the driver as 2.5 s and the coefficient of longitudinal fraction as 0.36, the value of ascending gradient (%) is