Test: Viral Hepatitis- 1 - NEET PG MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Viral Hepatitis- 1
Which of the following is used for laboratory diagnosis of alcoholic hepatitis? (AIIMS Nov 2018)
Which is true regarding hepatitis C infection? (JIPMER May 2018)
There are 3 to 5% healthy hepatitis B carriers in India who are asymptomatic. They have the risk of developing HCC in future due to: (AIIMS Nov 2017)
Which of the following serum markers for liver fibrosis can replace the need for liver biopsy? (AIIMS May 2017)
A patient is being evaluated for jaundice and liver fibrosis. His AST = 87 IU/mL and ALT = 81 IU/mL. His scrological tests are given below. Which of the following is the next step in the diagnosis? (AIIMS Nov 2016)

Which of the following virus is not transmitted by percutaneous transfer? (Recent Question 2016-17)
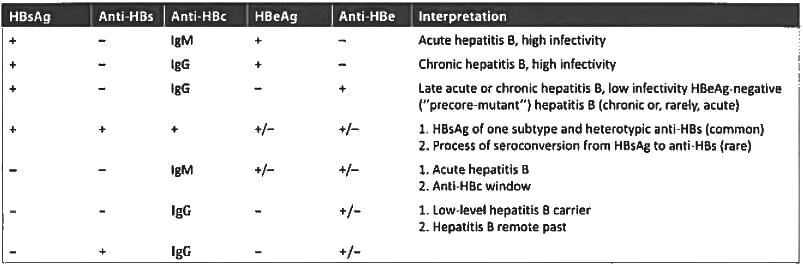
Which of the following viral markers signifies the ongoing viral replication in the case of Hepatitis-B infection? (UPSC 2015)
A person is HBsAg positive, but Anti-HBs Ab is negative. What should be the next step? (AIIMS May 2015)
Drug of choice for hepatitis B: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
HbsAg Carrier state is not associated with: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Most common route of transmission of hepatitis C: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Incubation period of hepatitis B is:(Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Best site of giving hepatitis B vaccine is: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
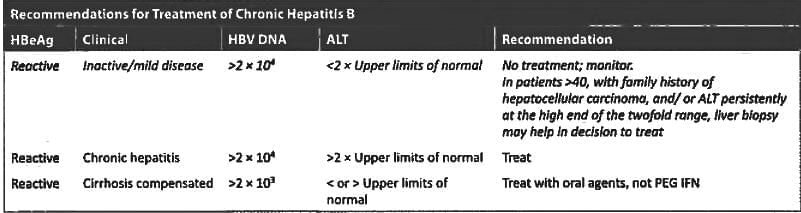
Patient comes for blood donation but he has Hbs Ag and HbeAg positive, and serum transminases level is normal. What would be the next management? (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
A 55-year-old male patient was diagnosed to have chronic hepatitis C. He responded to treatment with interferon. However, after one year of follow up he showed a relapse of disease. Which of the following would be the next most appropriate choice? (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
A HBs Ag carrier mother with anti Hbe Antibody positive in blood the chances of hepatitis in newborn is: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Most common genotype of hepatitis B in cirrhosis in North India: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
All of the following are true regarding chronic active hepatitis, except: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Which one of the following markers in the blood is the most reliable indicator of recent hepatitis B infection?
In a patient with fever, nausea and pain in right hypochondrium for 6 hours. Liver is not palpable. Most probable diagnosis is: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Which statement is wrong regarding Hepatitis B? (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Which is not transmitted via breast milk? (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
The marker of hepatitis B in the window period is: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Earliest manifestation of hepatitis B infection: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Fulminant hepatitis is commonest seen with? (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
A 30-year-old patient presents with H/O antibodies to HCV for 6 months duration and his AST/ALT is normal. There is no symptom or stigmata of liver disease. The most appropriate approach: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Which one of the following is transmitted non-parenterally: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Why pre-transfusion testing does not decrease the incidence of hepatitis? (JIPMER Nov 2014)