Test: Voltage Divider - GATE MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Voltage Divider
If there are 3 Resistors R1, R2 and R3 in series and V is total voltage and I is total current then Voltage across R2 is
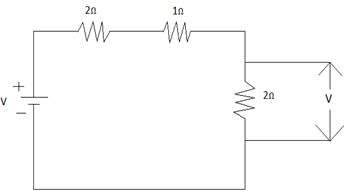
Calculate Voltage across 2Ω Resistor where supply v = 10 volts.

R1 = 1Ω, R2 = 3Ω, R3 = 5Ω and R4 = 7Ω connected in series. Total voltage = 20V, Current I, V2 =?
Voltage division is necessary for parallel resistance networks
An ideal voltage source is that which has an internal resistance
An ideal voltage source and internal resistance is an example of the
For a voltage source to be neglected, the terminals across the head should be ___________.
Voltage source and terminal voltage can be related as ___________.
A practical voltage source can also be represented as ___________.
A voltage source is having an open-circuit voltage of 200 V and internal resistance of 50Ω is equivalent to a current source of ___________.














