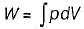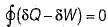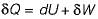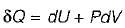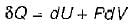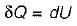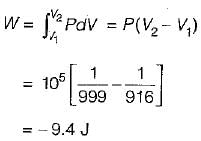Test: Work & Heat Transfer - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Work & Heat Transfer - 2
Which one of the following thermodynamic process approximates the steaming of food in a pressure cooker?
Heat transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume is equal to
The maximum amount of mechanical energy that can be converted into heat in any process
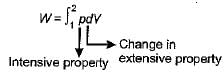
The expression for work done during a process 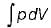 is applicable for
is applicable for
A paddle wheel used for stirring a liquid contained in a tank supplied 5000 kJ of work and during the stirring operation the tank lost 1500 kJ of heat to the surroundings. If the tank and liquid are considered as a system the change in its internal energy will be
The change in enthalpy of a closed system is equal to the heat transferred, if the reversible process takes place at constant
Which one of the following statement holds good for the equation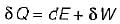
Change in internal energy in a reversible process occurring in a closed system is equal to the heat transferred, if the process occurs at constant
300 kJ of heat is supplied at constant temperature of 500 K, to a heat engine. The heat rejection takes place at 300 K. The following result are obtained (a) 210 kJ (b) 180 kJ (c) 150 kJ. Identify whether result is a reversible cycle. Irreversible cycle or impossible cycle respectively
Match List-1 with List-11 and select the correct answer using the codes given below.
List - I
A. Work done
B. Thermal equilibrium
C. Internal energy
D. No work and heat interaction
List - II
1. Point function
2. Path function
3. Isolated system
4. Equality of temperature
Codes:
A B C D
(a) 2 4 1 3
(b) 2 3 4 2
(c) 3 1 2 4
(d) 4 2 3 1
A 2 kW electric resistance heater submerged in 5 kg water is turned on and kept on for 10 min. During the process 300 kJ of heat is lost from the water the temperature rise of water is
One kg of ice at 0°C is completely melted into water at 0°C at 1 bar pressure. The latent heat of fusion of water is 333 kJ/kg and densities of water and ice at 0°C are 999 kg/m3 and 916 kg/m3 respectively. What are the approximate values of work done and energy transferred as heat for the process respectively.
It is desired to bring about a certain change in the state of a system by performing work on the system under adiabatic conditions.
Match the following:
A. Heat I. State function
B. Internal energy II. Path function
C. Work
D. Entropy
2 kg of steam in a piston-cylinder device at 400 kPa and 175°C undergoes a mechanically reversible, isothermal compression to a final pressure such that the steam becomes just saturated. What is the work, W, required for the process?
Data:
T = 175°C;
P = 400 kPa
v = 0.503 m3/kg
u = 2606 kJ/kg
s = 7.055 kJ/kgK
Saturated vapour, v = 0.216 m3/kg
u = 2579 kJ/kg, s = 6.622 kJ/kgK