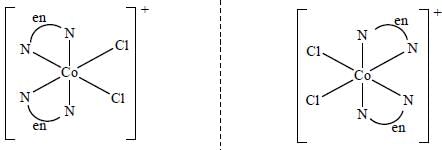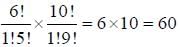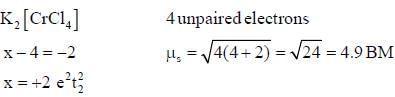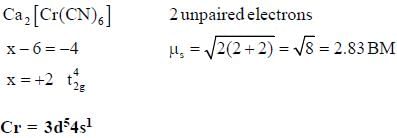Transition Metals & Coordination Compounds - GATE Chemistry MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test GATE Chemistry Mock Test Series - Transition Metals & Coordination Compounds
The ligand which can act as an ambidentate ligands in its complexes is
Which one of the following lias the lowest value of magnetic moment?
The magnetic moment of Cr2+ (gas) can be calculated by using the formula
The complex which absorbs lowest energy for its transition is
The π-acidity order of the following ligands is
Which of the following complexes shows orbital contribution to the magnetic moment?
The crystal field splitting energy value_________cm-1, for [Ti(h2O)6]+3 that has an absorption maximum at 492 nm.
Crystal field splitting energy Δ0 for [ Cr (NH3)6]2+ is 10200 cm-1. The Δt for [Cr(NH3)4]2+ is ___________cm-1.
The number of spinels having equal number of A2+ and B3+ ions in octahedral and tetrahedral voids are________
NiCr2O4, FeCr2O4, CO3O4, CrFe2O4, AlMg2O4, NiGa2O4
The number of complexes shows orbital contribution to the magnetic moment are:_________
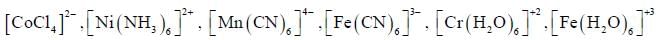
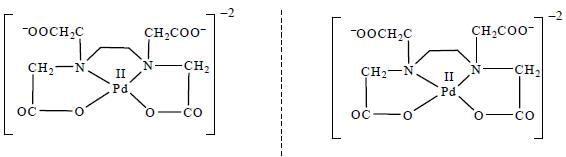
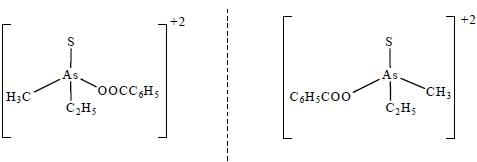
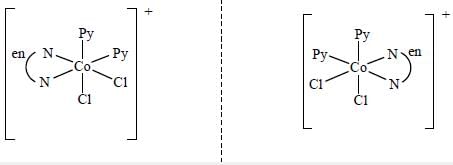
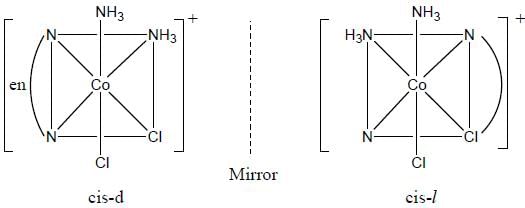
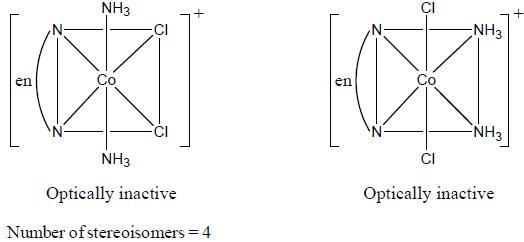
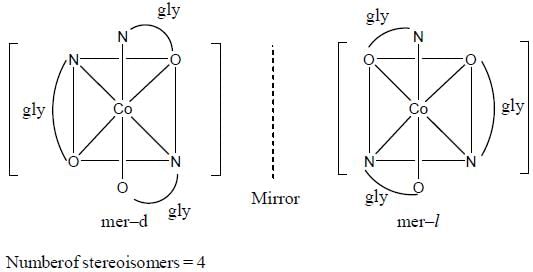
Which one of the following pair of complexes shows equal number of stereoisomers
The increasing order of inertness of the following complexes is
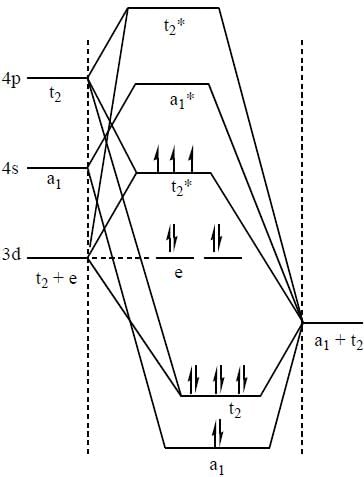
According to molecular orbital theory, the electronic configuration of [CoC14]2- ion is
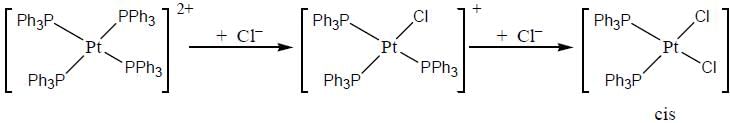
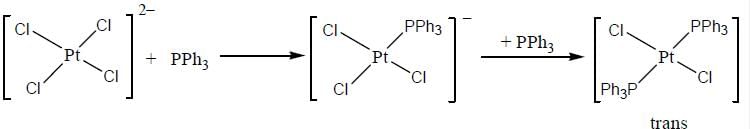
Predict tlie products (X) and (Y) in the following reaction:
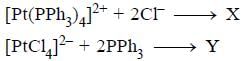
Consider the following reaction sequence
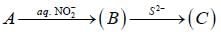
Conect set regarding A, B are C is
Treatment of alkaline solution of A with 30% H2O2 , leads to formation of red colour complex B. The The correct set regarding A and B is /are
The rate of electron transfer in 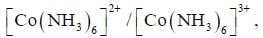 system compare to
system compare to 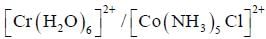 system is
system is
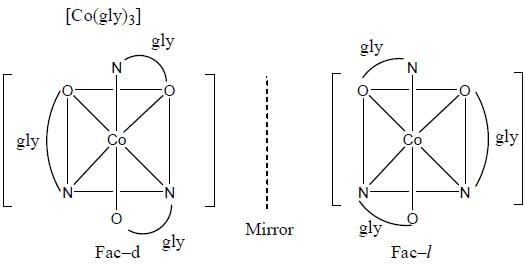
The number of complexes among the following show optical isomerism are_______________.
Number of micro states for 3p13 d1 configuration is_________________
The following complexes K2[MC14]J and C a[M( CN )6] have spin only magnetic moment o f 4.9 BM and 2.83 BM. The electrons present in valence shell d-orbital of neutral gaseous atom of M are______.
|
20 docs|37 tests
|



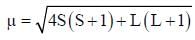
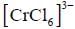 shows lowest energy transition
shows lowest energy transition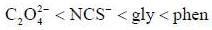
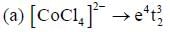
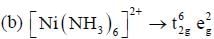
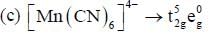
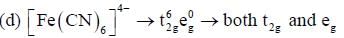
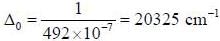
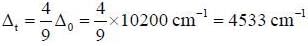
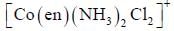
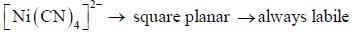
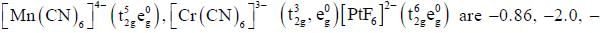
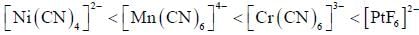

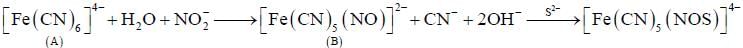
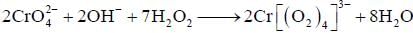
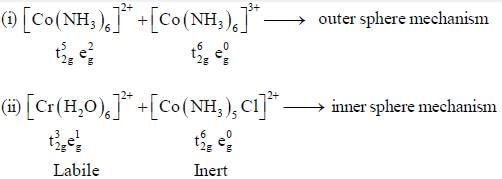 In reaction (ii). there is a briding ligand present with makes the reaction more feasible than (i) Thus, electron transfer in (ii) reaction occurs taster than (i)
In reaction (ii). there is a briding ligand present with makes the reaction more feasible than (i) Thus, electron transfer in (ii) reaction occurs taster than (i)