UGC NET Paper 1 Mock Test - 4 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series 2025 - UGC NET Paper 1 Mock Test - 4
Assertion: When engaging in meta-communication, addressing nonverbal cues like tone of voice and body language is just as important as focusing on the literal meaning of the words spoken.
Reason: Nonverbal cues often convey emotional subtext and hidden messages that can significantly alter the intended meaning of the spoken word.
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: Nyaya school of Indian philosophy is one of the six orthodox Darsanas.
Statement II: Nyaya school denies the existence of Isvara (God) as the efficient cause of the universe.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A key objective of the Paris Agreement under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is to:
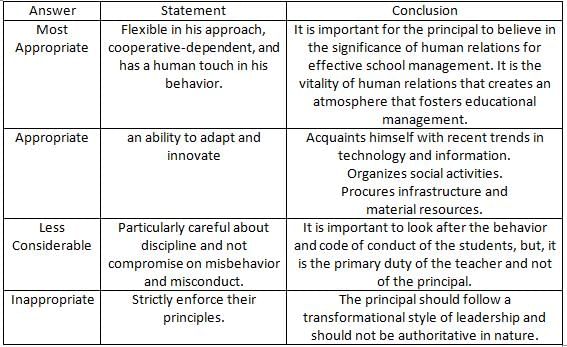
A good principal/teacher in educational institutions is one who
Which of the following statements is true regarding the two contrary propositions below?
Proposition 1: All birds can fly.
Proposition 2: No birds can fly.
Experiential learning can aid students to:
A. Broaden their worldview
B. Develop problem-solving skills
C. Improve public speaking skills
D. Neglect the importance of traditional learning methods
E. Inhibit individual creativity
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Point sources of water pollution are :
(A) Underground coal mines
(B) Run-off from farm fields
(C) Sewage treatment plants
(D) Run-off from roads and construction sites
(E) Power plants
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Find the ratio of the total number of girls who like both ice creams in school A and boys who like both ice creams in school E.
If 25% of boys & 20% of girls who like vanilla ice cream from school D caught a fever and 40% of total students who like chocolate ice cream from the same school caught the fever. The total number of ill students who like vanilla ice cream is what per cent more than the total number of ill students who like chocolate ice cream
What is the average number of boys who likes chocolate ice cream from all five schools?
What does the phrase "from each according to his ability, to each according to his need" aim to encapsulate within the context of communism?
In the global context, how has communism influenced socioeconomic reforms, as per the passage?
Based on the information in the passage, which of the following statement is correct?
In the context of the passage, what does the term "utopian" refer to?
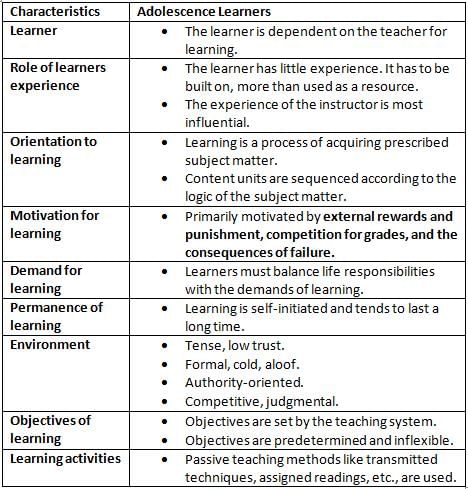
What is the best way to motivate adolescent learner?
The connotational aspect of a message in communication is:
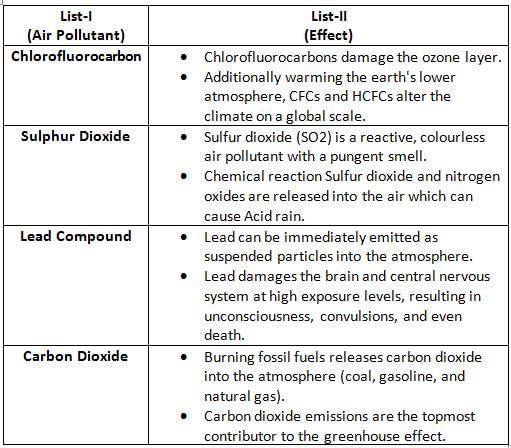
Chlordecone and Pentachlorobenzene, sometimes seen in the news are related to :
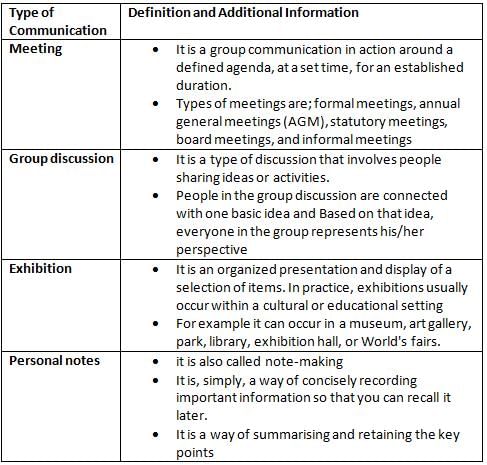
Which of the following will help to overcome communication barriers?
Match the List-I with List-II and select the correct option given below.
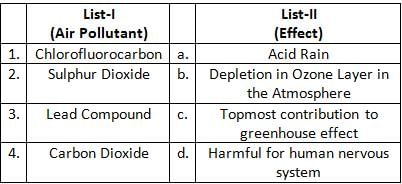
Match List I with List II
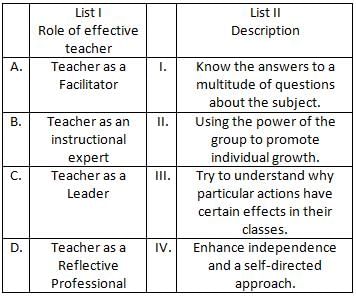
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Consider the following statements about the ancient Indian philosophy of Nyaya :
1. It is supposed to be founded by Gautama.
2. It is based on the concept of atomic theory.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Match List I with List II :
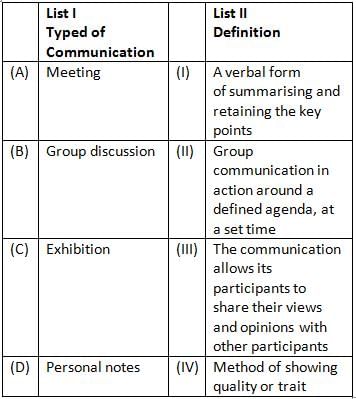
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
In India National Ambient Air Quality Monitoring (NAAQM) programme was initiated by:
|
92 docs|125 tests
|