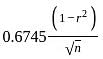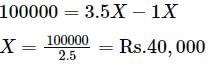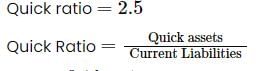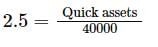UGC NET Paper 2 Commerce Mock Test - 5 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series - UGC NET Paper 2 Commerce Mock Test - 5
Given below are two statements:
One is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.
Assertion ‘A’: When holding company holds more than 50% (but not whole) shares of a company, then the holders of the rest of shares will be known as "Minority".
Reason ‘R’: Minority interest is calculated by considering proportionate shares and reserves of Holding Company.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Which of the following is NOT a method for calculating or ascertaining the amount of purchase consideration?
1. Net Payment Method
2. Net Assets Method
3. Gross Receipts Method
4. Share Exchange Method
Read the following statements :
(i) “Working Capital is the amount of funds necessary to cover the cost of operating the enterprise.”
(ii) “Circulating capital means current assets of a company that are changed in the ordinary course of business from one form to another.”
Consider the following statement about the Call Money market -
1. It is an inter-bank money market which is borrowed and lent for one day.
2. Collateral is not required to borrow money to call money market.
Select the correct answer using the code given below-
Indicate the item which appears under the sub head, short-term provisions:
The probable error of the coefficient of correlation (r) is calculated by which one of the following formulae?
Which of the following is 'true' regarding the Prudence Principle of Accounting?
Read the following statements :
(i) “Working Capital is the amount of funds necessary to cover the cost of operating the enterprise.”
(ii) “Circulating capital means current assets of a company that are changed in the ordinary course of business from one form to another.”
Direction: In the question given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Mark your answer as per the codes provided below.
Assertion (A): One can be sure about the future course of action by making good plans.
Reason (R): Planning brings certainty in the future course of actions of an organization.
Which of the following is not necessary for promotion from within?
In India a scheduled commercial bank is one which is
Following are the information for a house property:
Municipal value - Rs. 4,50,000
Fair rental value - Rs. 5,00,000
Standard rent - Rs. 4,80,000
Actual rent - Rs. 4,20,000
What is the gross annual value of the house property?
The most important component of the promotion mix to be used for industrial goods is?
Choose the correct option based on the equation given.
Current Ratio =3.5; Quick/Liquid ratio =2.5; Working Capital is Rs.100000.
Inventories are:
Right to information includes the right to:
1. inspect works, documents, records.
2. take notes, extracts or certified copies of documents or records.
3. take certified samples of material
4. obtain information in forms of printouts, diskettes, floppies, tapes, video cassettes or in any other electronic mode or through printouts.
Choose the correct codes:
Which of the following does not adversely impact the sustainability of Italy’s debt?
I. The rate offered on the bonds has increased when compared to the past.
II. The current rate offered on bonds is around the average rate of the existing debt.
III. Most of the debt is short to mature in terms of maturity.
Which of the following could be a possible reason for the line- ‘Foreigners are also unlikely to have suffered much direct harm from the fall in bond prices’?
I. Italy’s huge public-debt market gives it a decent weight in global bond indices.
II. Foreign investors have cut their Italian holdings from €473bn to €250bn during the last year.
III. Exposure of banks outside Italy has fallen by almost half since 2009, to €133bn.
Which of the following may be an ethics code?
|
92 docs|125 tests
|