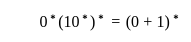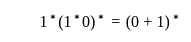UGC NET Paper 2 Computer Science Mock Test - 10 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series 2025 - UGC NET Paper 2 Computer Science Mock Test - 10
In a paging system, it takes 30 ns to search Translation Look-aside Buffer (TLB) and 90 ns to access the main memory. If the TLB hit ratio is 70%, then the effective memory access time is
In propositional logic, P ↔ Q is equivalent to (Where ~ denotes NOT)
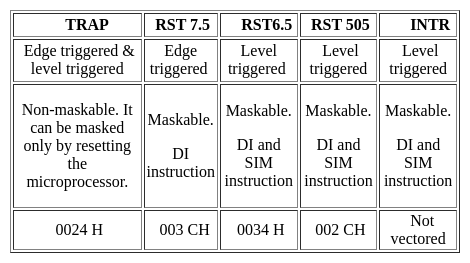
Which of the following 8085 microprocessor hardware interrupts has the lowest priority?
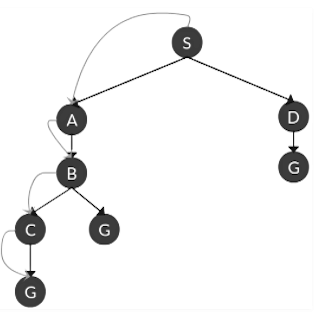
Given the language L = {ab, aa, baa}, which of the following strings are in L * ?
1) abaabaaabaa
2) aaaabaaaa
3) baaaaabaaaab
4) baaaaabaa
The regular expression 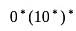 denotes the same set as
denotes the same set as
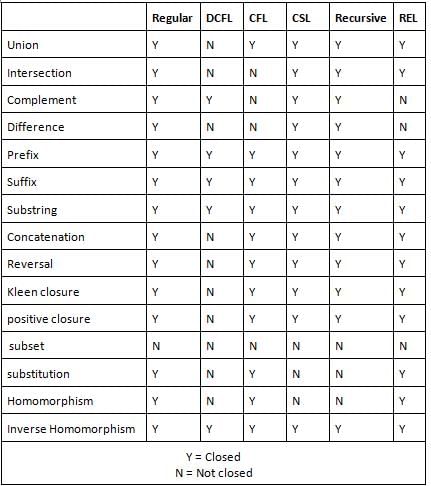
Which of the following statements about Regular Expression is/are incorrect?
A. The union of two regular expressions is also a regular expression
B. The concatenation of two regular expressions is also a regular expression
C. The iteration of a regular expression is also a regular expression
A stack-based CPU organization uses_______ address instructions
How much memory is required to implement z-buffer algorithm for a 512 × 512 × 24 bit-plane image
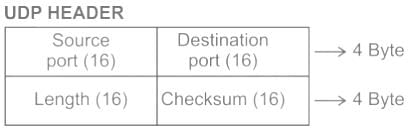
Which one of the following fields is present in both TCP header and UDP header?
Consider the following code segment to find the nth Fibonacci number:
fib(n)
{
if(n==0) {return 0;}
if(n==1) {return 1;}
else {return(fib(n-1) + fib(n-2);}
}
The time complexity of the above code and time complexity of the same problem solved using dynamic programming are ______ and ____ respectively.
A binary tree T has n leaf nodes, the number of nodes of degree 2 in T is:
If a logical address space of 128 pages of 1024 words each is mapped onto a physical memory of 64 frames, then the number of bits in logical space and physical address space in bits are respectively
A cache memory needs an access time of 30 ns and main memory 150 ns, what is the average access time of CPU (assume hit ratio = 80%)?
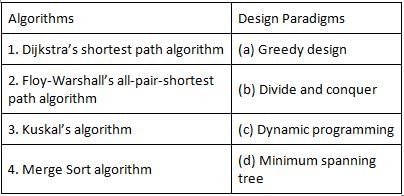
Given below are some famous algorithms and some algorithm design paradigms
A language _______ is supported by MS .Net platform.
If the boundary is specified in a single color, and if the algorithm proceeds pixel by pixel until the boundary color is encountered is called-
Consider a good system for the representation of knowledge in a particular domain. What property should it possess?
Which of the following is a back-end language?
DML language is used to ____________.
To set the line-width attribute the following command is used:
What is the space complexity of Depth-first search?
Which of the following that determines the need for the Circular Queue?
Which of the following is an incorrect activity for the configuration management of a software system?
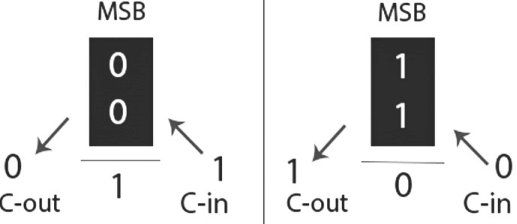
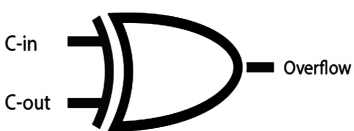
In a normal n-bit adder, to find out if an overflow as occurred we make use of ________.
We can check the attribute values by:
Depth-first search always expands the ______ node in the current fringe of the search tree.
ZooKeeper is especially fast in ___________ workloads.
|
92 docs|125 tests
|