UGC NET Paper 2 Computer Science Mock Test - 2 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series 2025 - UGC NET Paper 2 Computer Science Mock Test - 2
Which of the following scheduling algorithms may cause starvation?
a. First-come-first-served
b. Round robin
c. Priority
d. Shortest process next
e. Shortest remaining time first
b. Round robin
c. Priority
d. Shortest process next
e. Shortest remaining time first
The following statements (S1 and S2) pertain to the compiler in a computer.
S1 : It is a system software to convert source language program into target language program.
S2 : It validates the input program to the source language specification – produces error messages /warnings.
Choose the correct option
Which of the following statement(s) is/are FALSE?
(i) There exists a recursively enumerable language whose complement is not recursively enumerable.
(ii) If a language L is recursive, then its complement is NOT recursive.
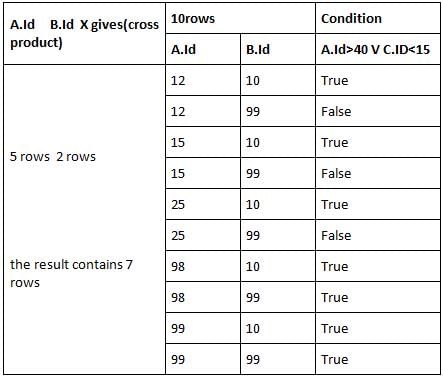
How many tuples does the result of the following relational algebra expression contain? Assume that the schema of A∪B is the same as that of A.
(A∪B) ⋈ A.Id > 40 ∨ C.Id < 15 C
What is the completion time of process P2 using shortest job first (pre-emptive)?
What is the waiting time of process P3 using shortest job first (pre-emptive)?
Consider the following statements regarding interrupts.
(I) If a process is interrupted during system call handling then the OS will crash.
(II) If a process is interrupted during system call handling then the process is moved to the READY queue.
(III) If an interrupt handler is interrupted, the OS will crash.
While of the above statements are true?
Consider the following AVL tree.
What will be the resultant AVL tree after insertion of node with value 20?
Consider the following statements:
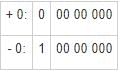
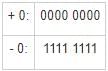
i) Zero has two representations in sign magnitude form and 1’s compliment form, but only one representation in 2’s compliment form.
ii) In sign magnitude form addition and subtraction are performed on separate hardware.
iii) Largest 3-bit number in 2’s compliment form is 3.
Which of the above statements is/are TRUE?
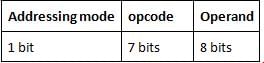
The basic computer has three instruction code formats, each format has 2 bytes. If addressing mode has 1 bit, operand has 1 byte then what is the size of opcode in a bit?
The individual pieces that make up a bitmapped image are often called _____________.
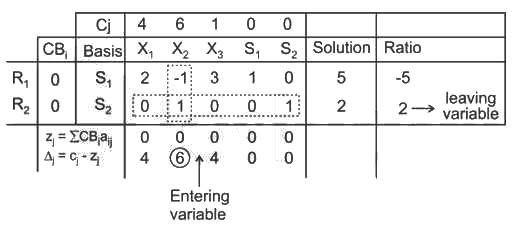
In the Simplex method if in pivot column all the entries are negative or zero when choosing leaving variable then
Which of the following statements are true?
S1: In a distributed DBMS, databases are stored at many locations with the use of a network, as compared to a centralized DBMS, which stores databases at a single location.
S2: When a centralized system fails, the entire system is brought to a halt, whereas in a distributed DBMS, If one system fails, the system keeps working with the other site.
Binding of instructions and data to memory addresses can be done at ____________.
Diagram which shows relationship between classes is termed as:
Most of the microcomputer's operating systems like Apple DOS, MS-DOS and PC DOS etc. are called disk operating systems because:
What is the name of the technique in which the operating system of a computer executes several programs concurrently by switching back and forth between them?
Which was the first widely used high-level language developed in 1957?
An expression builder is an access tool that controls an expression __________ for entering an expression.
A scheduler which selects processes from secondary storage device is called:
The interval from the time of submission of a process to the time of completion is termed as ____________.
Multiple repeaters in communication satellites are called:
What is the advantage of dynamic loading?
What is the main intent of project metrics?
|
92 docs|125 tests
|