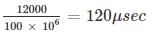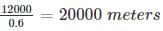UGC NET Paper 2 Computer Science Mock Test - 3 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series 2025 - UGC NET Paper 2 Computer Science Mock Test - 3
How many strings of 5 digits have the property that the sum of their digits is 7?
A software design pattern used to enhance the functionality of an object at run-time is
In 3G network, W-CDMA is also known as UMTS. The minimum spectrum allocation required for W-CDMA is
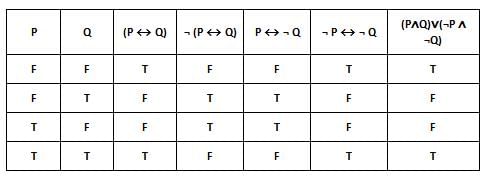
Which of the following is true?
I. ¬ (P ↔ Q) ≡ P ↔ ¬ Q
II. (P ↔ Q) ≡ (P ∧ Q) ∨ (¬ P ∧ ¬ Q)
III. (P ↔ Q) ≡ ¬ P ↔ ¬ Q
Direction: The item consists of two statements, one labelled as 'Statement (I)' and the other as 'Statement (II)'. You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the answers to these items using the code given below.
Statement (I): Pipeline processing cycle overlaps computer instruction cycle in execution for the performance improvement.
Statement (II): Pipelining is a technique of decomposing a sequential process into sub-operations, with each sub-process being executed in a special dedicated segment that operates concurrently with all other segments.
Which of the following properties of the circuits of a graph are correct?
1. The minimum number of branches possible in a circuit will be equal to the number of elements in a circuit.
2. There are exactly two paths between any pair of vertices in a circuit.
3. There are at least two branches in a circuit.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
The given statements are:
Statement A: Binary search takes a sorted/ordered list and divides it in the middle.
Statement B: If the middle element is greater than the key, the search repeats only in the second half of the list.
Statement C: Hash-based searching calculates the position of the key in the list using a formula called the hash function and the key itself.
Consider following Turing machine M,
M = (K, Σ, Γ, δ, q0, F) where
K = {q0, q1, q2, q3}
F = {q3}
Σ = {0, 1}
Γ = {0, 1, X, Y}
δ is defined as follows:
δ(q0, 0) = (q1, X, R)
δ(q1, 0) = (q1, X, R)
δ(q1, 1) = (q2, X, R)
δ(q2, 0) = (q1, X, R)
δ(q2, 1) = (q2, X, R)
δ(q2, Y) = (q3, halt)
The Language accepted by the above Turing Machine M is:
What is the smallest number of A’s that might be printed when this set of processes runs?
How many C’s are printed when this set of process runs?
A network with a ring topology having link bandwidths of 100 Mbps and propagation speed 2×108 m/sec. If packet size is 12000 bits, considering nodes do not introduce delay, then what would be the circumference if there was a node every 100 m and each node introduced 10 bits of delay?
Observe the HTML code given below and identify the line that will be ignored and not displayed by the browser :
<HTML>
<TITLE> Browser Test </TITLE>
<BODY>
<I> Test </l>
<!-- Testing -->
<B> Website </B>
</BODY>
</HTML>
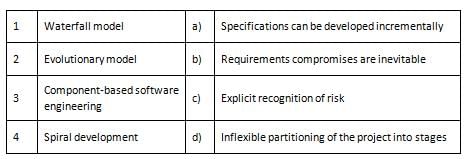
Which of the following is/are true about the software configuration management (SCM)?
I. It is written in the project planning phase.
II. In SCM, configuration identification ensures that changes to a system happen smoothly.
III. In SCM, configuration control involves deciding which parts of the system should be kept track of.Entities having a primary key are called?
Which of the following methods uses the concept that exponentiation is computationally inexpensive in the finite field?
_________________ allows us to infer that different members of classes have some common characteristics.
Which search is complete and optimal when h(n) is consistent?
Which one of the following is the size of int arr[9] assuming that int is of 4 bytes?
Coupling is a qualitative indication of the degree to which a module _____________.
Identify the language generated by the following grammar, where S is the start variable.
S → XY
X → aX | a
Y → aYb | ϵ
In 1985, the famous chess player David Levy beat a world champion chess program in four straight games by using orthodox moves that confused the program. What was the name of the chess program?
Which of the following is not an operating system?
The time and space complexity of BFS is (For time and space complexity problems consider b as branching factor and d as depth of the search tree.)
The choice between a bundled attribute or an unbundled attribute is made by switch called?
|
92 docs|125 tests
|