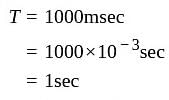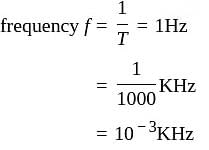UGC NET Paper 2 Computer Science Mock Test - 7 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series 2025 - UGC NET Paper 2 Computer Science Mock Test - 7
If the period of a signal is 1000 ms, then what is its frequency in kilohertz?
If there are n integers to sort and each integer has d digits and each digit is in the set {1, 2, ..., k}, then radix sort can sort the numbers in
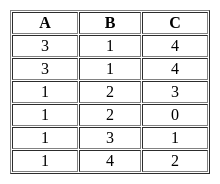
Consider the following ORACLE relations:
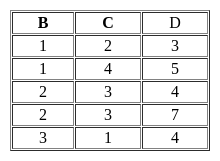
R(A,B,C)={〈1,2,3〉,〈1,2,0〉,〈1,3,1〉,〈6,2,3〉,〈1,4,2〉,〈3,1,4〉 }
S(B,C,D)={〈2,3,7〉,〈1,4,5〉,〈1,2,3〉,〈2,3,4〉,〈3,1,4〉 }
Consider the following two SQL queries
SQ1:
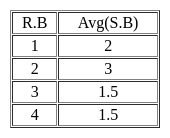
SELECT R.B,AVG(S.B)
FROM R, S
WHERE R.A=S.C AND S.D<7
GROUP BY R.B;
SQ2:
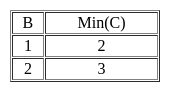
SELECT DISTINCT S.B,MIN(S.C)
FROM S GROUP BY S.B
HAVING COUNT (DISTINCT S.D)>1;
If M is the number of tuples returned by SQ1 and N is the number of tuples returned by SQ2 then M=______, N=______.
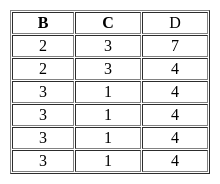
R(A,B,C)={〈1,2,3〉,〈1,2,0〉,〈1,3,1〉,〈6,2,3〉,〈1,4,2〉,〈3,1,4〉 }
S(B,C,D)={〈2,3,7〉,〈1,4,5〉,〈1,2,3〉,〈2,3,4〉,〈3,1,4〉 }
Consider the following two SQL queries
SQ1:
FROM R, S
WHERE R.A=S.C AND S.D<7
GROUP BY R.B;
SQ2:
FROM S GROUP BY S.B
HAVING COUNT (DISTINCT S.D)>1;
If M is the number of tuples returned by SQ1 and N is the number of tuples returned by SQ2 then M=______, N=______.
A company needs to develop digital signal processing software for one of its newest inventions. The software is expected to have 40000 lines of code. The company needs to determine the effort in person-months needed to develop this software using the basic COCOMO model. The multiplicative factor for this model is given as 2.8 for the software development on embedded systems, while the exponentiation factor is given as 1.20. What is the estimated effort in person-months?
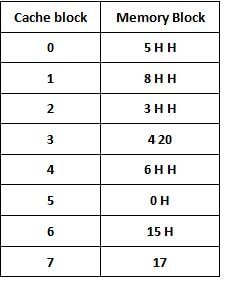
Consider a fully associative cache with 8 blocks. The memory block requests in the order.
5 8 5 3 4 6 3 8 5 6 0 15 6 17 20 15 0 8
If LRU is used for page replacement then which cache block will have memory block 20.
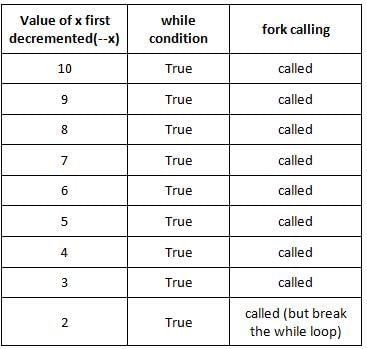
The process executes the code where x is an integer and x is initialized to 11
while(--x){
fork();
if(x == 2)
break;
}
The total number of child processes created is
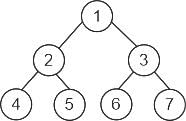
The above mentioned picture shows the:
A process executes the following code
for(i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
fork();
}
Total number of child processes created
Which of the following suffers from internal fragmentation?
- Paging
- Dynamic Partitioning
- Segmentation
- Fixed Partitioning
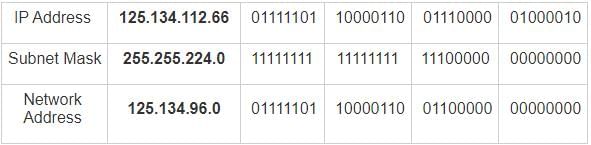
In a class B subnet, we know the IP address of one host and the mask as given below:
IP address = 125.134.112.66
Mask = 255.255.224.0
What is the first address (Network address)?
Which of the following phases of the compiler is machine independent?
A. Intermediate code generation
B. Target code generation
C. Intermediate code optimization
Following instructions were executed on a stack machine
PUSH X
PUSH X
MUL
POP Y
PUSH Y
PUSH Y
ADD
PUSH Y
MUL
POP Z
Value of Z isGiven:
Statement A: All cyclic groups are an abelian group.
Statement B: The order of the cyclic group is the same as the order of its generator.
Consider the following schedule for transactions T1, T2 and T3:
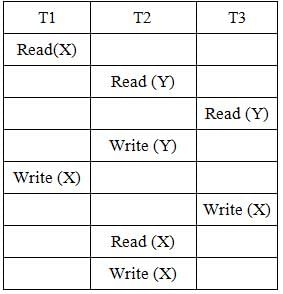
Which one of the schedules below is the correct serialization of the above?
Which of the following is expression is true if V1 is verification techniques, E is error detection techniques and V2 is validation techniques?
Which of the following is an application of depth-first search?
What is the minimum number of nodes in an AVL tree of height 5?
Parsing is categorized into how many types?
How do you represent “All dogs have tails”?
If the size of the stack is 10 and we try to add the 11th element in the stack then the condition is known as ___________.
Backtracking uses _______ node generation _______ bounding functions.
The range of the function f(x)=x−[x] where [x] represents the greatest integer less than or equal to x is:
Heap allocation is required for languages that:
The technique for selecting a new point depends upon _____________.
|
92 docs|125 tests
|