UGC NET Paper 2 Geography Mock Test - 9 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series 2025 - UGC NET Paper 2 Geography Mock Test - 9
Assertion (A): Mackinder’s theory of Heartland put forward a key formula “who rules Europe, commands the Heartland; who rules Heartland, commands the World Island; who rules the World Island command the world.”
Reason (R) : Mackinder’s formula offered Stalin’s strategy for territorial expansion and international supremacy.
Assertion (A): Behavioural geography laid importance to human activity in space, place and environment by studying it at the level of the individual person.
Reason (R): Geographers in the Western societies discovered the utility of mental maps in understanding why spatial planning failed in most cases.
Select the correct answer from the codes given below :
Consider the following statements:
1. Indian Mahogany species is well-known for its dense, redwood.
2. Mahogany can be found in almost every part of India.
3. Indian scientists discovered that the mahogany tree emits a sulphur compound that can help to reduce atmospheric warming caused by greenhouse gases.
4. Mahogany is considered a Mesophyte.
5. It is a fast-growing upright tree with an outwardly rounded symmetrical crown.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Himalayan Yew is an important plant for medicinal plants found in various parts of Himachal Pradesh and Arunachal Pradesh. It has been characterized as endangered by IUCN due to
1. Depletion of an inter-species gene bank of Yew.
2. Threat of bio-piracy.
3. Soaking of groundwater in areas where it is present.
i. Sunspots are features on the solar surface which appears as dark spot
ii. Sunspots are huge magnetic storms that occur on sun’s surface.
Choose the correct options:
a) L.C . King’s theory is based on the arid topography as well as the semi-arid regions of South Africa.
b) He mentioned that the profile of an ideal hillslope must consist of summit, scarp, slope and pediments.
c) According to King, the African landscape consisted of scarps which have steep slopes and varied in angle from 15-30 degree.
d) He also did explain the presence of Yardangs and Zuegen as prime features of the African Landscape.
Which of the following options are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. Humans can depart from directions as indicated by the natural environment.
2. Vice man follows nature’s plan only if he is wise.
Which of the above statement(s) corresponds with Neo-Determinism?What is the correct sequence of occurrence of various atmospheric layers from earth's surface?
1. Exosphere
2. Stratosphere
3. Troposphere
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
Consider the following statements and choose the correct option.
(A) An economically developed country could be a densely populated country.
(B) More women in population's base necessarily indicates their better status in society.
(C) Population pyramid is a tool to study the population composition of a country.
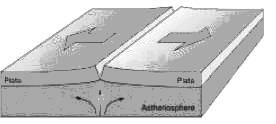
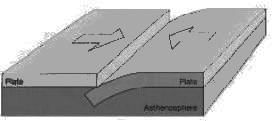
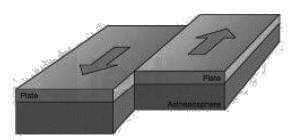
Consider the following statements regarding plate tectonics
1. Mid Ocean ridges and Rift Valley are characteristics of divergent plate boundaries
2. Convergent plate boundaries are constructive in nature.
3. San Andreas Fault is an example of Transform Plate boundary.
4. Zone of Subduction is associated with Divergent Plates.
Which of the is/are correct
What is the wind direction in a cyclone in southern hemisphere ?
Select the correct option(s) for the statement from the codes given below:
A region is more diverse culturally if it:
(a) has homogeneous population composition
(b) has heterogeneous population composition.
(c) receives voluminous in migration.
(d) is geographically isolated.
Critics of the Malthusian Theory argue that advancements in which field have mitigated the challenges predicted by Malthus?
a) Society is a mosaic of various modes of social processes and interactions.
b) Industrialization has always been a positive force in modernizing the society.
c) Competition as a social process has always been an universal action.
d) Accommodation goes hand in hand with cooperation and conflict.
Which of the following options are correct?
Match List-I with List-II
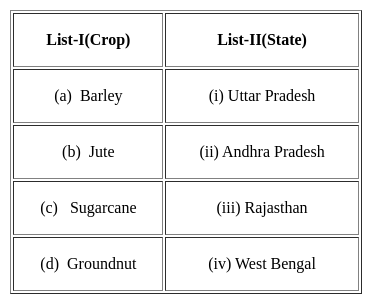
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following is not among the four coral reef regions of India identified by the Government for intensive conservation and management?
Identify the non Green-House Gas(GHG) from the following :
…………….. clouds are associated with rainfall, thunder and lightning
|
92 docs|125 tests
|