UGC NET Paper 2 Sociology Mock Test - 10 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series - UGC NET Paper 2 Sociology Mock Test - 10
Who among the following observed that the Chief Executives and the very rich are one and the same group in the U.S.A.?
Assertion (A): It is not merely equality under the law that determines that status of women in society.
Reason (R): Tradition and customs are involved in everyday social interaction.
Select the correct answer using codes given below:
_______ is an electrically powered and Remotely Operated Vehicle by DRDO.
An institution can be best described as a complex of:
________ denotes the functional significance of the actor for the social system.
Which factor is negatively correlated with modernization?
Which one of the following statements is true regarding the different aspects of 'Multiculturalism'?
I. Cosmopolitan Multiculturalism reflects the influence of globalization on culture.
II. Pluralism multiculturalism supports toleration i.e. willingness to accept those views with which it disagrees
III. Liberal Multiculturalism recognizes various values and believes in respecting them all
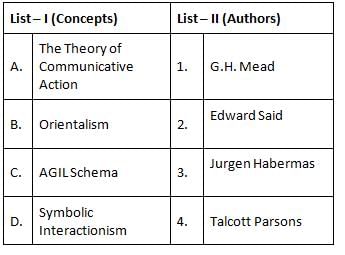
Which theory of Habermas is useful way to explore knowledge and its impact on students engagement ?
The term cultural relativism means:
(i) Any culture can be evaluated in absolute terms.
(ii) It refers to not judging a culture to a person's own standards.
(iii) It refers to a person's understanding about cultural practices of other groups in its own cultural context.
(iv) Different cultures are related to each other in terms of some universal elements.
Give answer from the options:
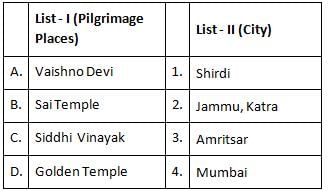
Match the key concept with its corresponding description.
Key Concepts
A. Historical Materialism
B. Dialectical Materialism
C. Class Struggle
D. Surplus Value
E. Communism
Corresponding Description
1. The ultimate stage where class distinctions and private property are abolished.
2. The conflict of opposing forces leading to historical progress.
3. Analysis of capitalist economies and the appropriation of surplus labor.
4. The driving force behind historical change based on changes in the mode of production.
5. Society divided into bourgeoisie and proletariat.
Answer:
Who among the following is related with Transactional Theory of Leadership?
A. Max Weber
B. Bernard M. Bass
C. Robert R. Blake
D. Abraham Maslow
The population census will have the primary data from:
Climate pledges under Paris Agreement cover what fraction of greenhouse gas emissions reduction needed to limit the global warming below 2°C?
Sociology is characterized by a perspective that places in the foreground.
Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): No society can be fully free from deviance
Reason (R): Deviance and conformity are the ongoing processes in society
Choose the correct answer from the following codes
Which among the following is not a cause of the growth of cities?
Which of the following does not correspond to characteristics of research?
Which sector has gained maximum from the 1991 LPG reforms?
The first newsprint paper mill in India was set up in:
With reference to India, consider the following statements:
1. There is only one citizenship and one domicile.
2. A citizen by birth only can become the Head of State.
3. A foreigner once granted citizenship cannot be deprived of it under any circumstances.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
|
92 docs|125 tests
|