UGC NET Paper 2 Sociology Mock Test - 4 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series - UGC NET Paper 2 Sociology Mock Test - 4
Radcliffe Brown consider sociology as a science of__________.
Which one of the following is not a characteristic feature of the bureaucratic authority?
_______refers the refurbishing or replacement of old buildings & new use of previously developed land in urban areas.
What was A. R. Desai's main focus of study?
Consider the following:
Assertion(A): Elections in India are a process by which the people of the country express their collective will.
Reason(R): People are true sovereigns governing the country.
Which of the following are the characteristics of the Bureaucratic model?
1. Distinction between office and person
2. Legitimization of authority by technical competence
3. Recognition of informal groups in official scheme
4. Encouragement of career and differentiated rewards
With the emergence of the agricultural Society:
The process by which an individual learns the culture of their society is known as:
Who defined culture is the "realm of styles, of values, of emotional attachment, of intellectual adventures"?
Who has defined 'culture as a body of shared understandings'?
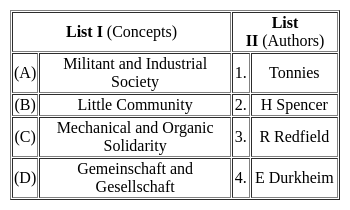
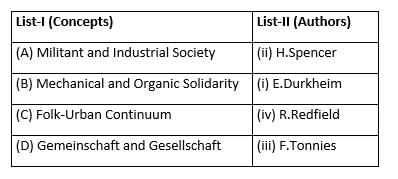
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below the lists.
A, B,C, and D are respectively.
Who has presented the view, ‘a historical approach that also makes possible generalizations about processes of social change’?
The concept ‘’Culture of Poverty’’ was introduced by:
Which of the following statements is not true according to Malinowski?
Which state of India became first to reserve a government job for HIV positive candidates?
Why did studies of political culture become more fashionable in the 1960s?
Who is known to have used the ‘Indological perspective’ in the study of Indian society?
(A) G. S. Ghurye
(B) Luis Dumont
(C) N. K. Bose
(D) M. N. Srinivas
Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
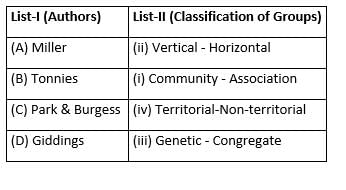
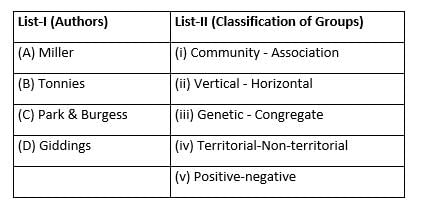
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below:
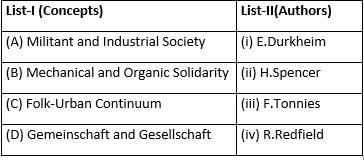
A, B, C, and D are respectively.
Direction: In the following question, the Assertions (A) and Reason (R) have been put forward. Read both the statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following:
Assertion (A): All groups are social networks.
Reason (R): All networks are not social groups.
Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
Who said, “ Economic Planning is a way of organizing and utilizing resources to maximum advantage in terms of defined social ends”?
|
92 docs|125 tests
|