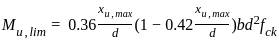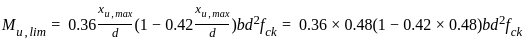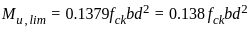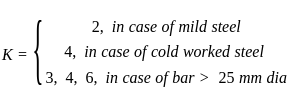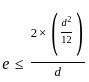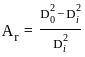UPPSC AE Civil Paper 1 Mock Test - 1 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UPPSC AE Civil Paper 1 Mock Test - 1
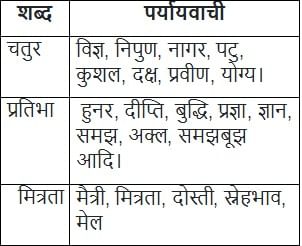
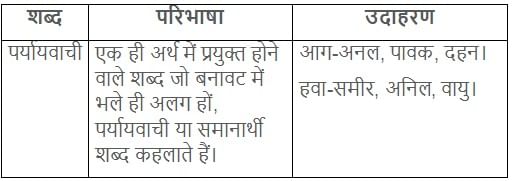
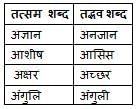
'प्रभंजन' निम्नलिखित में से किस शब्द का पर्यायवाची है -
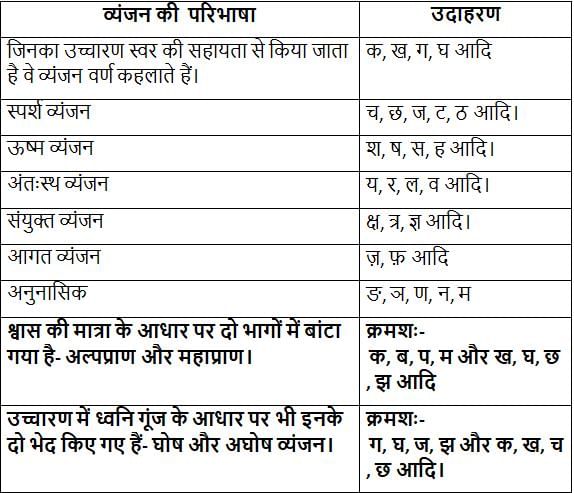
स्पर्श व्यंजन, कण्ठ्य ध्वनि, अघोष और महाप्राण ध्वनि है:
'समाज' शब्द में कौन-सा प्रत्यय जोड़कर 'सामाजिक' शब्द बना है?
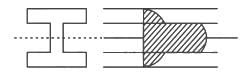
In a uniform I-section beam, where does the largest shear stress act ?
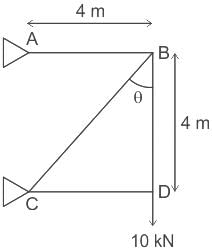
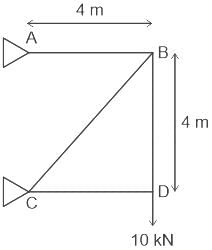
For the truss shown in figure (supports A & C are hinge type), the force in member AB and BC are respectively:
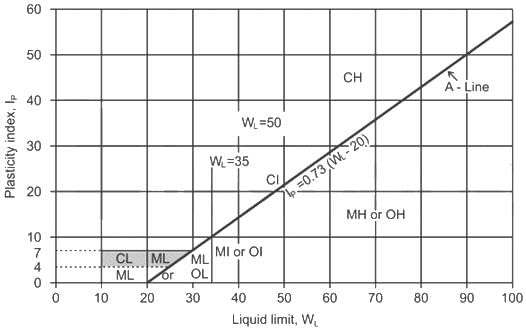
The soil has a liquid limit of 50%. Following the A-line, in the plasticity chart as per IS : 1498 – 1970, the corresponding plastic limit is :
As per IS 456 : 2000, in reinforced and plain concrete, for footings on piles, the thickness at the edge shall be NOT less than ________ above the top of piles.
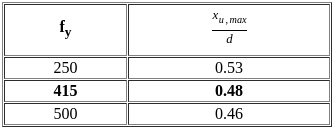
For a rectangular beam Limiting value of moment of resistance reinforced with Fe 415 is?
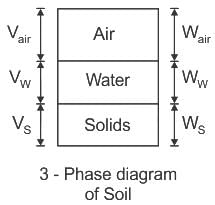
In a soil's three-phase diagram, the constituents of soil are:
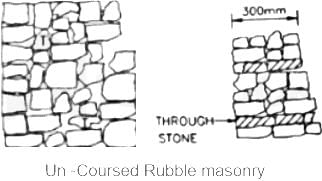
Which of the stone masonry is the cheapest, roughest and poorest form ?
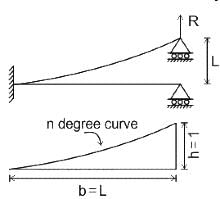
What is the area (m2) of the influence line diagram for the reaction at the hinged end of a uniform propped cantilever beam of span 'L' m?
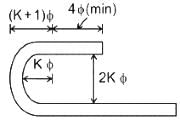
Internal radius of the bend for hooks of deformed bar should be for mild steel
The Kernel of a short column of rectangular cross section is a
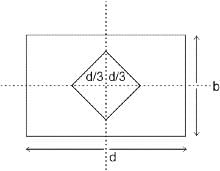
The area ratio of thin wall sampler should NOT normally exceed more than
According to IS 399-1963, the weight of timber is specified at
To provide safety against piping failure with a factor of safety of 5, what should be the maximum permissible exit gradient for soil with specific gravity of 2.5 and porosity of 0.35?
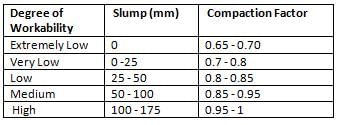
A compacting factor of 0.88 for a fresh concrete sample indicates a mix of