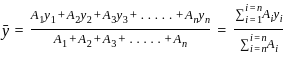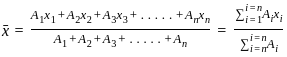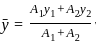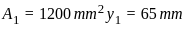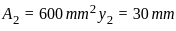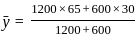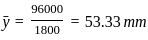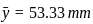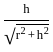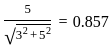UPPSC AE Civil Paper 1 Mock Test - 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UPPSC AE Civil Paper 1 Mock Test - 2
शब्द "तिरस्कार" का सही विशेषण रूप निम्नलिखित में से कौन-सा है?
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में से कौनसे शब्द की वर्तनी सही है?
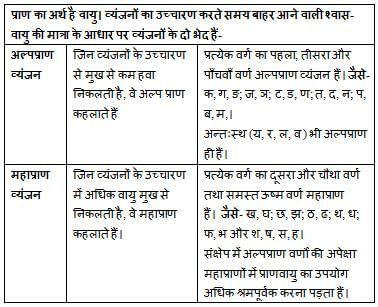
एक शब्द में महाप्राण व्यंजनों का प्रयोग नहीं हुआ है
अर्थ और प्रयोग की दृष्टि से एक मुहावरा गलत है
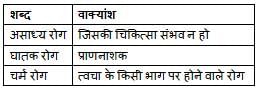
'वह (व्यक्ति) जिसने संन्यास ग्रहण किया हो' - इस वाक्यांश के लिए एक शब्द है
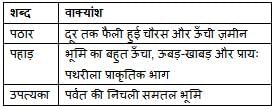
'पर्वत के ऊपर की समतल भूमि' के लिए एक शब्द है
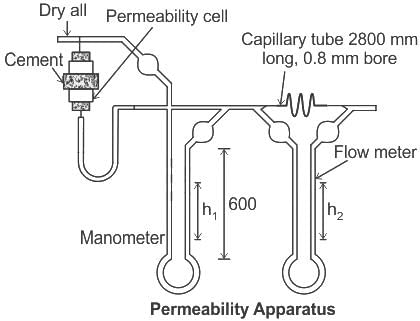
In the context of testing of cements in the laboratory, consider the following statements:
Statements I: The Blane method of determination of fineness is based on evaluation of the heat of hydration during the hydration process.
Statements II: The determination of initial and final setting times is based on change in penetration resistance over time due to continued hydration.
Which of the following is CORRECT?
Study the given statements with respect to characteristics of bending moment diagram (BMD) for beam and select the correct answer.
Statement A : If a beam is subjected to uniformly distributed load (UDL) throughout its span, the shape of BMD will be a cubic parabolic curve.
Statement B : If a cantilever beam is subjected to a uniformly distributed load (UDL) throughout its span the maximum value of bending moment will be at its mid-span.
______ are the temporary joints left between subsequent concreting operations, their position should be pre - planned before concreting is started.
The example of intermittent type equipment is
As per IS codes, the minimum characteristic yield strength for hot rolled high yield strength deformed bars is ____
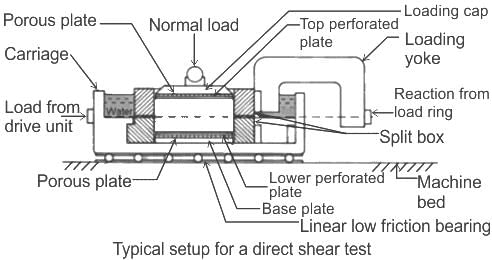
In the direct shear test conducted on soils, a proving ring is used to _______.
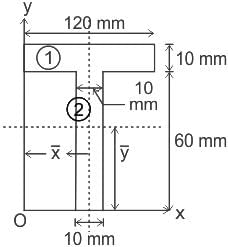
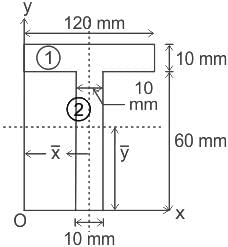
Calculate the value of y̅ (distance from line 'Ox' to centroid) for the T-section shown in the figure.
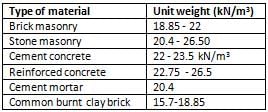
Unit weight of common burnt clay bricks in kN/m3 ranges between
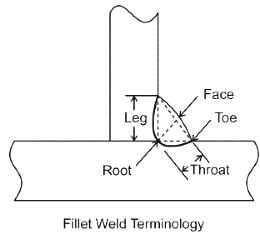
In a fillet welded joint, the weakest area of the weld is
Minimum tension steel in RCC beam needs to be provided to
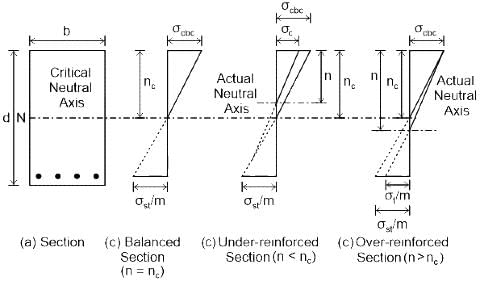
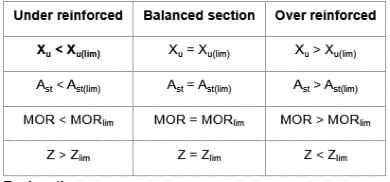
The actual neutral axis of under reinforced section is
The ratio of distance moved by effort to distance moved by load is called
Which of the following statements are correct?
A. Direct cost increases with duration.
B. Direct cost decreases with duration.
C. Indirect cost increases with duration.
D. Indirect cost decreases with duration.
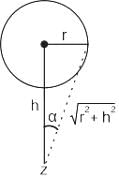
A load of 16 kN/m2 is uniformly distributed over a circular area of 6 m diameter at the ground surface. The vertical stress at a point P, which is at a depth of 5 m directly below the center of the loaded area will be
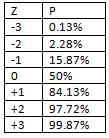
In PERT analysis, the probability of completion of the project in 40 days will be (given : earliest expected time, TE of last event is 40 days)
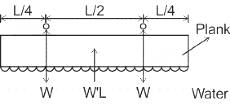
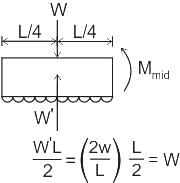
Two people weighing 'W' each are sitting on a plank of length 'L' floating on water at L/4 from either end, neglecting the weight of the plank the bending moment at center of plank is
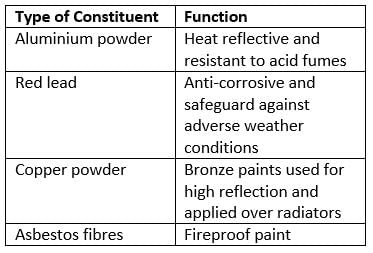
In fireproof paints, the main constituent is:



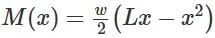
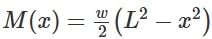
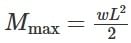
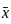 and
and 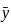 be the co-ordinates of the centre of gravity with respect to some axis of reference, then
be the co-ordinates of the centre of gravity with respect to some axis of reference, then