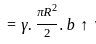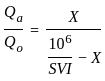UPPSC AE Civil Paper 2 Mock Test - 1 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UPPSC AE Civil Paper 2 Mock Test - 1
Who argued that “The Indian Constitution established indeed a system of Government which is at most quasi-federal, a unitary state with subsidiary features rather than a Federal States with unitary features"?
_____ was appointed as chairman of the State Reorganisation Commission in 1953.
Which of the following is a fundamental duty enshrined in Part IV-A of Constitution?
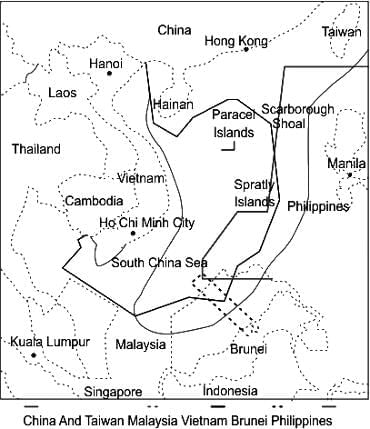
Which of the following sea is situated between the Philippines and Vietnam?
With reference to National Ayurveda Day 2021, which of the following statement is/are correct?
1. It was celebrated on 23rd October 2021.
2. Its theme was 'Ayurveda for Poshan'.
Select the correct answer from the code given below:
In India, the voting age was lowered from 21 to 18 years by which of the following Constitutional Amendment?
Plotting of inaccessible points on a plane table is done by
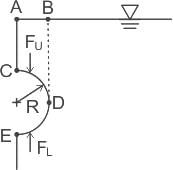
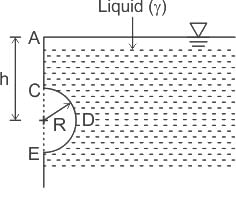
The net vertical force (F) on the submerged semicircular projecting structure CDE as shown in the figures will be?
Assume the structure has uniform width b into the paper and liquid has specific weight γ.
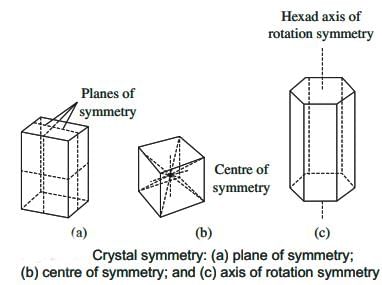
Which of the following statements correctly defines the Axis of Rotation Symmetry in crystal geometry?
In the activated sludge process, sludge volume index is used to decide
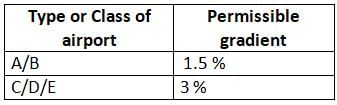
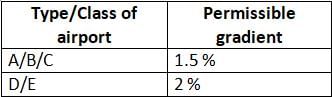
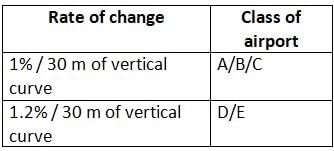
Identify the mis-matched pair about type of Airport and the maximum value of longitudinal gradient of a taxiway, as per ICAO.
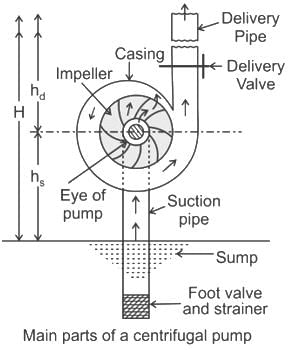
In a centrifugal pump, the liquid enters the pump
Any liquid, gaseous or solid substance which is discharged from any premises used for carrying on any industry, operation or process, or treatment and disposal system, other than domestic sewage is called
If a turbine develops 2515 kW at 240 rpm, the torque in the shaft is
Benkelman beam deflection method is used for the design of
Based on '30th' hourly volume, for how much percent time during the year can the designer willingly tolerate the unfavourable operating conditions?