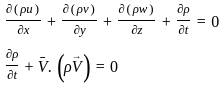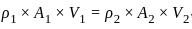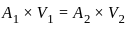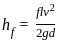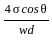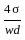UPPSC AE Civil Paper 2 Mock Test - 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UPPSC AE Civil Paper 2 Mock Test - 2
The main feature of the Kshatrapal form of governance in the Shaka Empire was _______.
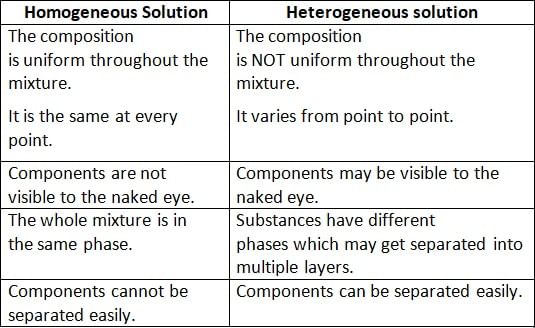
Which among the following is a homogenous solution?
The provision for Anti Defection Act is mentioned in which of the following Schedules of the Constitution of India?
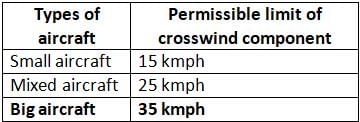
As per ICAO, for airports serving big aircrafts, the crosswind component should not exceed
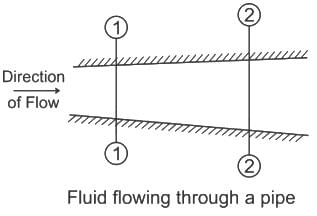
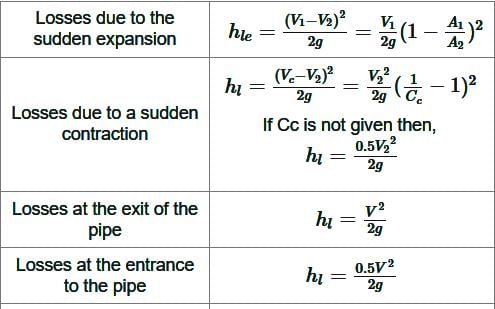
Equation of continuity is based on the principle of conservation of
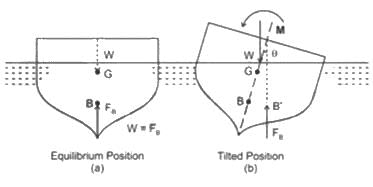
For a submerged body, if the centre of buoyancy coincides with the centre of gravity, the equilibrium is called
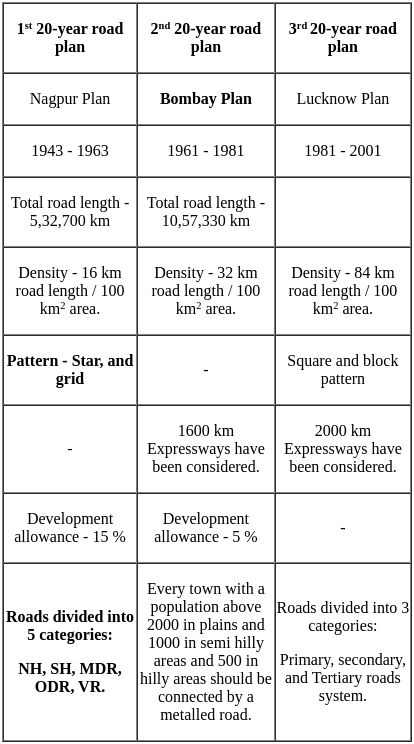
The second twenty year road plan is also called _______.
Which one of the following expresses the height of rising or fall of a liquid in a capillary tube?
Where w = Specific weight of the liquid, θ = Angle of contact of the liquid surface, σ = Surface tension, d = diameter of the capillary tube.
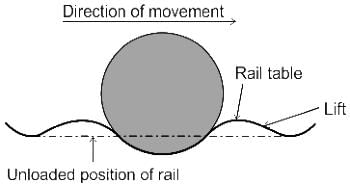
Gradients are compensated to the following extent on curves, on NG (now gauge) tracks, _____ per degree of the curve or _____ whichever is minimum
When the surface of the spillway is made to coincide with the shape of the lower nappe of free falling water jet, then it is known as ________
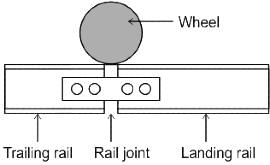
Which of the following methods of designation of crossing is mostly used in India?
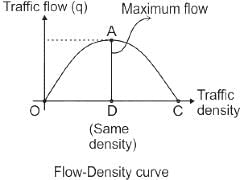
The product of traffic density and traffic speed is termed as
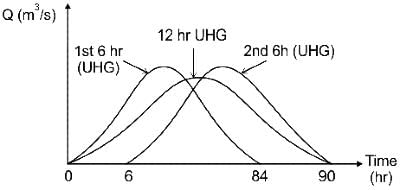
If the base period of a 6 hr. unit hydrograph of a basin is 84 hr. then, the base period of a 12 hr. unit hydrograph of the same basin will be
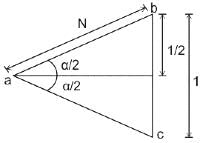
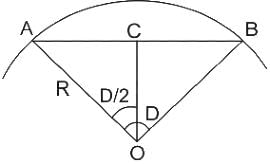
If the length of a chord/arc is 20 m in a curve, then the relationship between R and D in the curve will be
The unit power Pu of a turbine developing a power P under a head H is equal to