Triangles - Olympiad Level MCQ, Class 9 Mathematics - Class 9 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Triangles - Olympiad Level MCQ, Class 9 Mathematics
Q. In the given figure AD is the bisector of ∠A and AB = AC. Then ΔACD, ΔADB are congruent by which criterion?
In ΔABC if ∠B = ∠ C = 45°, which of the following is the longest side ?
In a ΔABC if ∠ A = 45° and ∠B = 70° then the shortest and the largest sides of the triangle are :-
In Δ ABC if ∠B = 45°, ∠ C = 65°, and the bisector of ∠BAC meets BC at P. Then the ascending order
of sides is :-
In a ΔABC if 2∠ A = 3 ∠ B = 6 ∠ C then ∠ A ∠ B ∠ C are :
By which congruency property, the two triangles connected by the following figure are congruent :-
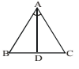
In ΔABC, AB = AC and AD is perpendicular to BC. State the property by which ΔADB ≌ADC :-
State the property by which ΔADB ≌ADC in the following figure :-
In the given figure if AD = BC and AD || BC, then :
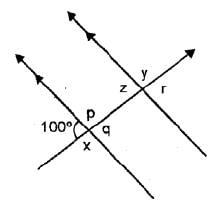
In the figure given below, find the measure of the angles denoted by x,y, z,p,q and r.
An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of two _________ angles :-
In the following, the set of measures which can form a triangle :-
Sum of any two sides of a triangle is always __________ third side in a triangle :-
Can 90°, 90° and 20° form a triangle ?
In the given figure it is given that AB = CF, EF = BD and Ð AFE = Ð DBC. Then DAFE congruent to DCBD by which criterion ?















