NEET Exam > NEET Tests > Chemistry Class 12 > Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - NEET MCQ
Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - NEET MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds
Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds for NEET 2025 is part of Chemistry Class 12 preparation. The Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds questions and answers have been
prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus.The Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds below.
Solutions of Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds questions in English are available as part of our Chemistry Class 12 for NEET & Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds solutions in
Hindi for Chemistry Class 12 course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds | 10 questions in 15 minutes | Mock test for NEET preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study Chemistry Class 12 for NEET Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - Question 1
Which one of the following is likely to give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution?
Detailed Solution for Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - Question 1
Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - Question 2
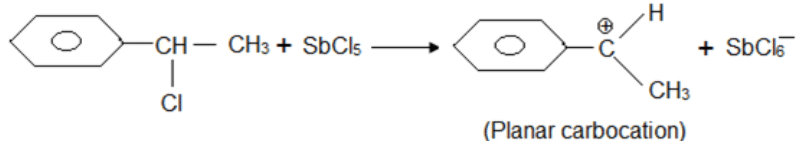
A solution of (–)-1-chloro-1-phenylethane in toluene racemises slowly in the presence of a small amount of SbCl5, due to the formation of
Detailed Solution for Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - Question 2
Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - Question 3
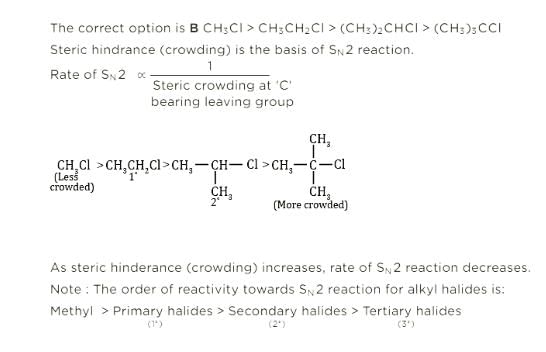
In SN2 reactions, the correct order of reactivity for the following compounds: CH3Cl, CH3CH2Cl, (CH3)2CHCl and (CH3)3CCl is
Detailed Solution for Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - Question 3
Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - Question 4
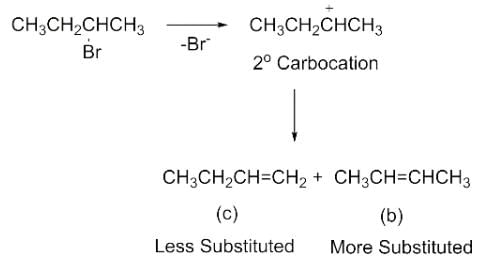
Elimination of bromine from 2-bromobutane results in the formation of
Detailed Solution for Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - Question 4
Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - Question 5
Which of the following is a tertiary halogenoalkanes?
Detailed Solution for Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - Question 5
Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - Question 6
Which of the following is not true about optical isomers?
Detailed Solution for Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - Question 6
Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - Question 7
Which of the following is not an aryl halide?
Detailed Solution for Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - Question 7
Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - Question 8
Pick up the correct statement about alkyl halides.
Detailed Solution for Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - Question 8
Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - Question 9
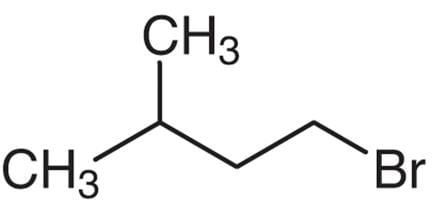
Which one of the following is 1-bromo-3-methyl butane?
Detailed Solution for Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - Question 9
Detailed Solution for Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds - Question 10
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|
Information about Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Characteristics of Halo Compounds, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice