Test: SN2 Reaction Basics - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - Test: SN2 Reaction Basics
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Which of the SN2 reaction is fastest?
A correct statement about transition state of SN2 reaction is
What is the correct increasing order of reactivity of the followings in SN2 reaction ?
I. CH2 = CHCH2 — Br
II. CH2 = CH— I
III. CH3CH2CH2 — I
IV. CH3OCH2CH2 — I
What is the correct increasing order of reactivity of the following in the SN2 reaction?
Consider the two lines shown in the diagram given below.
Q.
In a SN2 reaction, these two lines compare the effect of the
Consider the two lines shown in the diagram given below.
Q.
Which of the following apply appropriately to a SN2 reaction?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 9-14) This section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
In a SN2 reaction rate of reaction depends on
Consider the following SN2 reaction,
Q.
Which of the following could increase the reactivity (rate) of reaction ?
A SN2 reaction involves back side attack of nucleophile at the α-carbon of substrate because
1-chlorobutane is more reactive than 2-chloro-2-methyl propane in a SN2 reaction because
Consider the reaction given below.
Q.
The correct statement(s) applicable to the above reaction is/are
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three Questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
The general mechanism of a SN2 reaction is as follows.
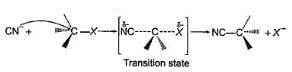
Factors that limit the rate of reaction are steric hindrance at α-cabron of substrate and strength of C—X bond. Any factor which stabilises transition state increases the rate of reaction.
Q. Consider the following SN2 reaction,
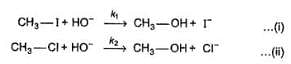
Which of the following energy diagram is correctly labelled?
The general mechanism of a SN2 reaction is as follows.
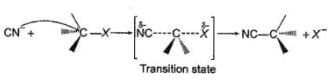
Factors that limit the rate of reaction are steric hindrance at α-cabron of substrate and strength of C—X bond. Any factor which stabilises transition state increases the rate of reaction.
Q.
In the previous question, under identical reaction condition, i.e. tem perature, concentration of substrate and nucleophile, the correct relationship between rate constant is
The general mechanism of a SN2 reaction is as follows.
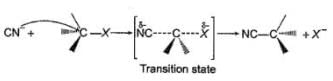
Factors that limit the rate of reaction are steric hindrance at α-cabron of substrate and strength of C—X bond. Any factor which stabilises transition state increases the rate of reaction.
Q.
Which of the following is not a correct representation of SN2 reaction ?
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 18-20) This section contains 3 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Consider the following reaction,
Q.
The above reaction was started taking equal concentrations of ethyl iodide and NaOH. After 1.0 h, concentration of iodoethane is dropped to (1/3)rd of initial value. By what factor, the rate of reaction would have been decreased by the same time?
Under identical experimental condition, how many of the following substrate react at faster rate with aqueous NaOH than 2-bromobutane as substrate?





Consider the following compound,
Q. If the above compound is treated with excess of NaCN(aq), how many CN- group would be incorporated by SN2 reaction?
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|




















