Test: Reaction of Alcohols - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test NCERT Based Tests for NEET - Test: Reaction of Alcohols
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
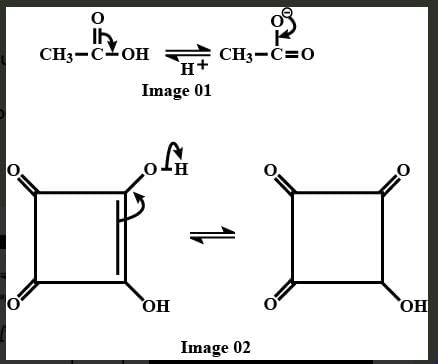
The correct order of acidic strength of the following alcohols is
Among the alkenes which one produces tertiary butyl alcohol on acid hydration
Which compound given below has the highest solubility in water ?
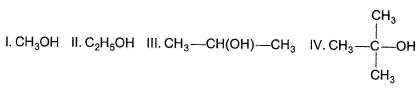
What is the correct increasing order of acidity of the following?
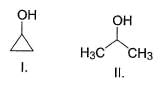
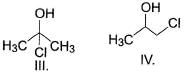
What is the order of solubility of the following in water?
Which of the following can be used for the distinction of ethanol from phenol?
Consider the following reaction,
The above reaction can best be brought about by
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 9-12) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Consider the compound shown below,
Select the correct statement(s).
Consider the following substituted ethanol G—CH2CH2OH
Which group(s) when present as G gives greater equilibrium of gauche conformer than its anti counterpart ?
Which of the statement given below concerning 3-methyl-2-butanol is/are correct ?
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 13-15) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
An organic compound X (C10H12O3) is not soluble in water or NaHCO3. A solution of Br2 in CCI4 is decolourised by X forming C10H12O3Br2. X on controlled ozonolysis followed by the treatm ent with (CH3)2S gives Y (C8H8O3) and C2H4O2. Y can also be obtained by reaction between ortho methoxy phenol with CHCI3 in KOH solution followed by acid hydrolysis.
Q.
What is the correct structure of X?
An organic compound X (C10H12O3) is not soluble in water or NaHCO3. A solution of Br2 in CCI4 is decolourised by X forming C10H12O3Br2. X on controlled ozonolysis followed by the treatm ent with (CH3)2S gives Y (C8H8O3) and C2H4O2. Y can also be obtained by reaction between ortho methoxy phenol with CHCI3 in KOH solution followed by acid hydrolysis.
Q.
If X is treated with cold HBr, the major product would be
An organic compound X (C10H12O3) is not soluble in water or NaHCO3. A solution of Br2 in CCI4 is decolourised by X forming C10H12O3Br2. X on controlled ozonolysis followed by the treatm ent with (CH3)2S gives Y (C8H8O3) and C2H4O2. Y can also be obtained by reaction between ortho methoxy phenol with CHCI3 in KOH solution followed by acid hydrolysis.
Q.
What would be the major product if X is treated with cold concentrated H2SO4?
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 16-19) This section contains 4 questions. When worked out w ill result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
How many reagents from the list given below, gives visible change when treated with 2-propanol?
If 4-methyl-2-pentene is refluxed with dilute H2SO4, hydration reaction takes place. In principle, how many different alcohols are formed ?
Consider the following reaction, how many different organic products are formed at the end of the reaction?
If pentane-2, 4-diol is treated with excess of p-toluene sulphonyl chloride followed by C2H5ONa/C2H5OH, dienes are formed by E2 elimination reaction. In principle, how many different dienes are formed ?
Which of the following alcohols is oxidized to a ketone by PCC (Pyridinium Chlorochromate)?
|
684 tests
|