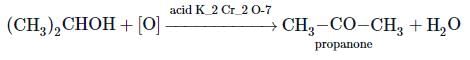Test: Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers
Ketones are reduced to the corresponding alcohols by catalytic hydrogenation to form
Which of the following reagents can be used to oxidise primary alcohols to aldehydes?
What is the correct order of reactivity of alcohols in the following reaction?
Phenol can be distinguished from ethanol by the reactions with _________.
Primary alcohols are prepared by reduction of carboxylic acids. Though lithium aluminium hydride is a strong reducing agent, it is not used in the reaction. Because
The reaction C2H5ONa + C2H5I → C2H5OCH5 + NaI is known as
How many alcohols with molecular formula C4H10O are chiral in nature?
Preparation of ethers by acid dehydration of secondary or tertiary alcohols is not a suitable method.
Aldehydes are reduced to the corresponding alcohols by addition of hydrogen in the presence of catalysts to form
An organic compound containing oxygen, upon oxidation forms a carboxylic acid as the only organic product with its molecular mass higher by 14 units. The organic compound is ______.
The process of converting alkyl halides into alcohols involves_____________.
Which of the following compounds will react with sodium hydroxide solution in water?
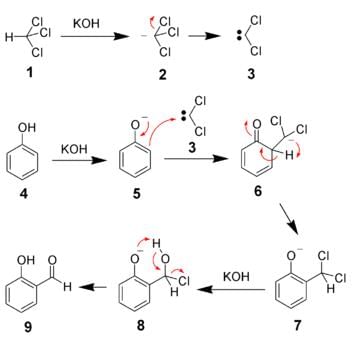
The reaction which involves dichlorocarbene as an electrophile is
An organic compound X is oxidised by using acidified K2Cr2O7. The product obtained reacts with Phenyl hydrazine but does not answer silver mirror test. The possible structure of X is
Methyl bromide is converted into ethane by heating it in ether medium with
One of the following alcohol is a poison and Ingestion of even small quantities can cause blindness and large quantities causes even death.
A hydrocarbon C5H10 does not react with chlorine in dark but gives a single monochloro compound C5H9Cl in bright sunlight. The hydrocarbon is
Which of the following species can act as the strongest base?