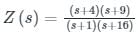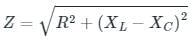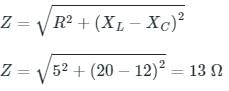One time: Test: Impedence - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - One time: Test: Impedence
If the load impedance is 20 - j20, the power factor is -
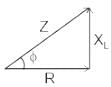
If the resistance of the coil is 15 ohms, impedance of the coil is 25 ohms, the inductive reactance will be:
The phase voltage and current across a load element are 100.0 ∠45° V and 5.0 ∠15° A. respectively. Determine the impedance and admittance of the load.
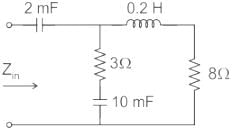
What is the input impedance of the circuit, if the circuit operates at ω = 50 rad/s ?
A resistance, an inductance and a capacitance are connected in series. The values of R, XL and XC are 20 Ω, 30 Ω and 10 Ω respectively. The net reactance of the circuit is:
Calculate the total impedance for a circuit having the following values:
Resistance = 5 Ω
Inductance reactance = 20 Ω
Capacitance reactance = 8 Ω
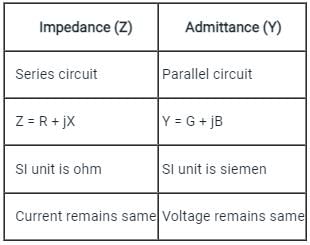
In a parallel circuit, current in each impedance is_______
In a parallel circuit, we consider admittance instead of _________
Impedance is a complex quantity having the real part as _______ and the imaginary part as ______


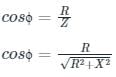
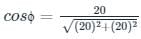



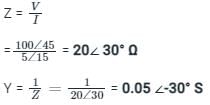
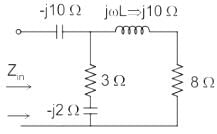
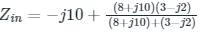
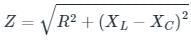
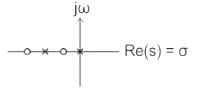
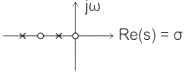
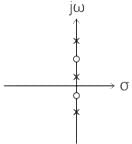
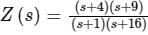 is a driving-point impedance, it represents an
is a driving-point impedance, it represents an