Test: Anatomy of Flowering Plants - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 11 - Test: Anatomy of Flowering Plants
Aerating pores in the bark of plants is known as
In which type of leaves does the abaxial epidermis contain more stomata than the adaxial epidermis?
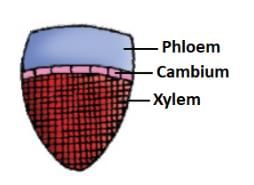
The vascular bundle shown in the diagram is most likely to be seen in:
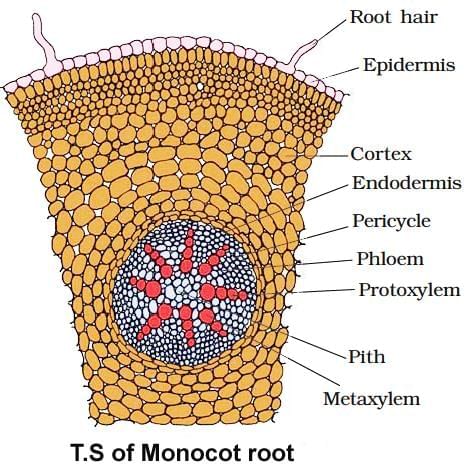
Which of the given figure represents the internal structural details of a monocot root?
How many of the following constitute the stele?
Vascular bundles, pericycle, endodermis, pith, cortex, epidermis
In leaves, the ground tissue consists of thin-walled chloroplast containing cells are called
Which of the following do not undergo anysecondary growth?
Assertion (A): Plant tissues are classified into meristematic and permanent types, which contribute to their various functions.
Reason (R):
The main functions of plant tissues include food assimilation, storage, and mechanical support.
|
180 videos|362 docs|148 tests
|