Test: Body Fluids & Circulation - 2 - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Body Fluids & Circulation - 2
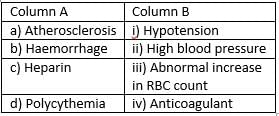
Blood plasma proteins :
i. decrease in their level causes excessive absorption of water from tissues into blood.
ii. they maintain osmotic pressure.
i. decrease in their level causes excessive absorption of water from tissues into blood.
ii. they maintain osmotic pressure.
The mass of tissue seen in the left corner of the right atrium close to the atri-ventricular septum is
Manoj has AB blood group, so he will have the following antibodies in his blood plasma :
When a person suffers from chest pain :
i. the reason for this suffering is decreased blood flow and simultaneously lowered oxygen supply to an area of the heart.
ii. deprived of oxygen, myocardium opts for alternative pathways i.e. anaerobic respiration and its byproduct ethanol causes the pain.
Blood pressure is expressed as the ratio of systolic over diastolic pressure. The difference between systolic and diastolic pressure is called pulse pressure. What will be its value for a normal healthy adult?
As Soham, ages with chronic CAD the lumen of his coronary artery may get nearly completely obstructed Result is flow of blood to heart tissue is restricted such that the tissue receives inadequate supply of oxygen rich blood and this condition is diagnosed as :
In our blood :
i. Granulocytes which constitutes maximum percentage of total leucocytes are neutrophils.
ii. Elevated number of neutrophils in blood indicates an acute infection such as appendicitis.
In the human heart :
i. The valve between right atrium and right ventricle is tricuspid while valve between left atrium and left ventricle is mitral valve.
ii. Openings of the right and the left ventricles into the pulmonary artery and the aorta are guarded by semilunar valves.
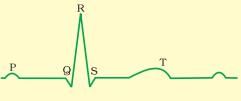
iii. ‘Lub’ the first sound which is low pitched is caused by the closure of semilunar valves while ‘Dub’ the second sound which is high pitched is caused by the closure of bicuspid and tricuspid valves.
Meghna suffers from allergic asthma. After a blood test her leucocyte count displayed an abnormal increase in the number of :
Which of these is not included in the vascular system?
Each cardiac cycle takes 0.8 seconds to occur. Calculate how many cardiac cycles occur in 4 minutes ?
Which of these organs are situated in the thoracic cavity?
When blood clot starts contracting, a pale yellow fluid starts oozing out. Its name and composition is :
Which of these structures is close to the AVN?
Ramesh has Rh antigen and Anti-A as well as Anti-B antibodies in his blood. During blood transfusion he can receive blood from :
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: The coagulum is formed of network of threads called thrombins.
Statement II: Spleen is the graveyard of erythrocytes.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below: