Test: Human Excretory System - 2 - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 11 - Test: Human Excretory System - 2
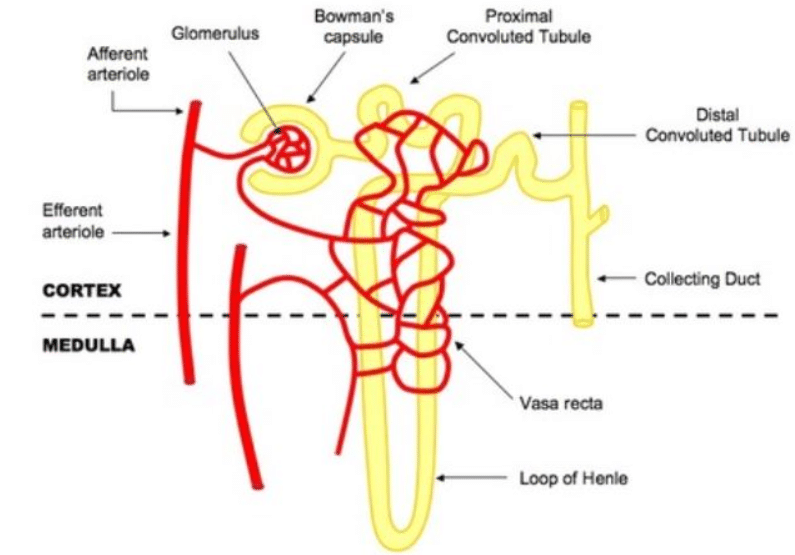
In cortex area of kidney all structure are found except :–
Malpighian corpuscles are present in :–
[RPMT 2001]
The blood vessel taking blood into Bowman's capsule is
What triggers the release of renin from the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA)?
What will happen if the diameter of the afferent arteriole is less than efferent arteriole?
What hormone regulates the reabsorption of water in the distal parts of the kidney tubule?
Difference between glomerular filtrate and plasma is of
[DPMT 85]
Excretory products of mammalian embryo are eliminated by-
[CPMT-81, APMS 85]
A condition of failure of kidney to from urine is called -
[DPMT 84]
The filtrate from the glomerulus contains
[CPMT 75]
Nitrogenous waste products are eliminated mainly as -
[AIPMT 91]
Which blood vessel contains the least amount of urea
[CPMT 84]
Ammonia is the main nitrogenous excretory material in
[DPMT 85]
Assertion (A): The kidneys regulate glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through various mechanisms including the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA).
Reason (R): The JGA releases renin in response to a decrease in GFR, which helps to increase glomerular blood flow and restore normal GFR.
|
180 videos|367 docs|148 tests
|