Test: Human Excretory System (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Human Excretory System (NCERT)
Which of the following statements is correct?
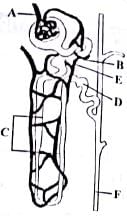
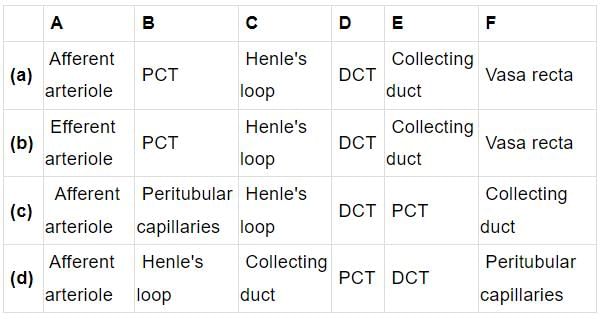
Select the option that correctly identifies the parts lateral from A to F in the given figure of nephron.


Match Column-I with Column-II and select the correct option from the codes given below.
Column-I
(A) Delivers blood to glomerulus
(B) Carries urine to pelvis
(C) Collects filtrate form Bowman's capsule
(D) Loop of Henle
Column-II
(i) Ascending and descending limbs
(ii) Renal artery
(iii) Collecting duct
(iv) PCT
Column-I
(A) Delivers blood to glomerulus
(B) Carries urine to pelvis
(C) Collects filtrate form Bowman's capsule
(D) Loop of Henle
Column-II
(i) Ascending and descending limbs
(ii) Renal artery
(iii) Collecting duct
(iv) PCT
The dotted appearance of cortex of kidney is do
Which of the following is not correct with respect to human kidney?
_______ produces urea as the excretory substance in the human body.
What are Protonephridia primarily concerned with in terms of function?
Which excretory structures are responsible for nitrogenous waste removal in insects like cockroaches?
Where are the kidneys located in the human body?
What is the primary function of the collecting duct in the kidney?
What physiological effect does the release of Atrial Natriuretic Factor (ANF) have on blood vessels?
What substances are eliminated through the secretions of sweat glands and sebaceous glands in the skin?














