NEET Exam > NEET Tests > Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - NEET MCQ
Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - NEET MCQ
Test Description
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1
Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 questions and answers have been prepared
according to the NEET exam syllabus.The Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 below.
Solutions of Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 questions in English are available as part of our course for NEET & Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 solutions in
Hindi for NEET course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 | 20 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for NEET preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for NEET Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 1
Example of artificial auxins are:
(a) IPA
(b) IBA
(c) NAA
(d) 2, 4 -D
(b) IBA
(c) NAA
(d) 2, 4 -D
Detailed Solution for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 1
Detailed Solution for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 2
Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 3
Which of the following is essential for fruit ripening?
Detailed Solution for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 3
Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 4
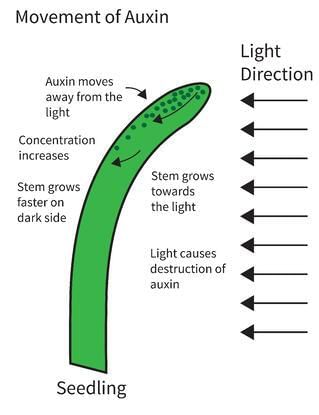
Which of the following effects of auxins is of wide application?
Detailed Solution for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 4
Detailed Solution for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 5
Detailed Solution for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 6
Detailed Solution for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 7
Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 8
What is the effect of abscisic acid (ABA) on plant stomata?
Detailed Solution for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 8
Detailed Solution for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 9
Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 10
Which of the following statements about plant growth regulators is true?
Detailed Solution for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 10
Detailed Solution for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 11
Detailed Solution for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 12
Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 13
Growth is primarily affected by two climatic factors which are
Detailed Solution for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 13
Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 14
Coconut milk contains a cytokinin called ____ which promotes plant growth.
Detailed Solution for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 14
Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 15
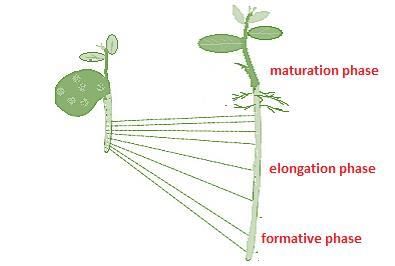
In a growing plant, the first phase during the process of growth is
Detailed Solution for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 15
Detailed Solution for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 16
Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 17
The natural plant hormones were first isolated from
Detailed Solution for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 17
Detailed Solution for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 18
Detailed Solution for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 19
Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 20
Plants follow different pathways in response to the environment or phases of life to form different kinds of structures. This ability is called:
Detailed Solution for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 - Question 20
Information about Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Plant Growth & Development - 1, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF