Plant Physiology MCQ - Biotechnology Engineering (BT) MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2025 - Plant Physiology MCQ
The circadian rhythms of plants and animals are maintained by which of the following?
Which of the following is a driving force for movement of water from soil to root during absorption of water by a plant?
Which of the following statement is true with regard to guard cells?
The conversion of ACC to ethylene during ethylene biosynthesis is catalysed by which of the following?
During photorespiration in plants, carbon dioxide is produced when glycine is converted to serine in
Which of the following is incorrect with regard to active transport?
Among the Following, Which Acid is a Derivative of Carotenoids?
Which of the following reactions are catalysed by enzyme nitrogenase?
The number of water molecules required to generate one O2 in the light reaction of photosynthesis is _______[Answer in integer]
The number of ATP molecules required for fixing one molecule of CO2 in C4 plants is __________ [Answer in integer]
The number of electrons released during photolysis when 1 molecule of oxygen is evolved are__________[Answer in integer]
Number of turns of Calvin cycle required to make one molecule of glucose is __________ [Answer in integer]




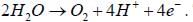 Thus 4 protons and 4 electrons are released to evolve 1 molecule of oxygen.
Thus 4 protons and 4 electrons are released to evolve 1 molecule of oxygen.
















