Test: Casting Processes - 3 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Topicwise Question Bank for Mechanical Engineering - Test: Casting Processes - 3
Which of the following materials can be used for making patterns?
1. Aluminium
2. Wax
3. Mercury
4. Lead
1. Aluminium
2. Wax
3. Mercury
4. Lead
Match the List-I (Equipment) with List-II (Functions):
List-I
A. Hot chamber machine
B. Muller
C. Dielectric baker
D. Sand blasting
List-II
1. Cleaning
2. Core making
3. Die casting
4. Annealing
5. Mixing
Codes:
A B C D
(a) 3 5 2 1
(b) 4 2 5 3
(c) 4 2 3 1
(d) 3 5 1 2
List-I
A. Hot chamber machine
B. Muller
C. Dielectric baker
D. Sand blasting
List-II
1. Cleaning
2. Core making
3. Die casting
4. Annealing
5. Mixing
Codes:
A B C D
(a) 3 5 2 1
(b) 4 2 5 3
(c) 4 2 3 1
(d) 3 5 1 2
Which of the following materials requires highest shrinkage allowance?
Directional solidification can be achieved by providing
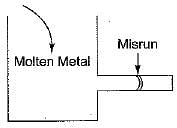
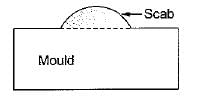
The casting defect which is not caused by the high pouring temperature of melt is
Which of the following materials has more shrinkage allowances
While pouring molten metal in the mould of the molten metal does not appear in the riser. It indicates
In solidification of metal during casting, compensation for solid contraction is
Which of the following casting mould uses metal moulds?
The casting method adopted for ornament toys of nonferrous alloys is
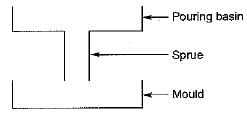
Bottom gating system is sometimes preferred in casting because
Which one of the following processes produces a casting when pressure forces the molten metal into the mould cavity.
In a green sand moulding process, uniform ramming leads to
Which of the following are the most likely characteristics in centrifugal casting?
The centrifugal casting method is used for casting articles of
Consider the following ingredients used in moulding
1. Dry silica sand
2. Clay
3. Phenol formaldehyde
4. Sodium silicate
Q. These used for shell moulding include
|
45 videos|314 tests
|