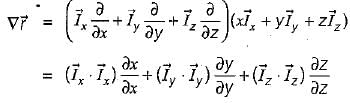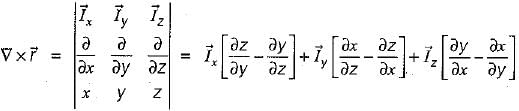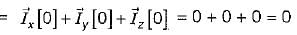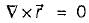Test: Vector Analysis- 2 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Topicwise Question Bank for Electrical Engineering - Test: Vector Analysis- 2
What is the value of constant b so that the vector
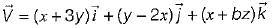 is solenoidal?
is solenoidal?
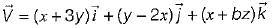 is solenoidal?
is solenoidal?Match List-I with List-ll and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
A. Gauss’s divergence theorem
B. Stroke’s theorem
C. The divergence
D. The curl
List-ll
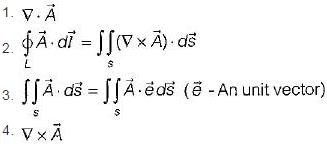
Assertion (A): Vector differential operator is a vector quantity and it signifies that certain operations of a differentiation are to be carried out on the scalar function following it.
Reason (R): Vector differential operator posses properties similar to ordinary vectors
Consider the following statements:
1. Divergence of a vector function 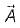 at each point gives the rate per unit volume at which the physical entity is issuing from that point.
at each point gives the rate per unit volume at which the physical entity is issuing from that point.
2. If a vector function ϕ represents temperature, then grad ϕ or ∇ϕ will represents rate of change of temperature with distance.
3. The curl of a vector function A gives the measure of the angular velocity at every point of the vector field.
Assertion (A): The Gauss’s divergence theorem permits us to express certain integrals by means of surface integrals.
Reason (R): Gauss’s divergence theorem states that “the surface integral of the curl of a vector field taken over any surface s is equal to the line integral of the vector field around the closed periphery (contour) of the surface.
If 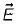 is any vector field in cartesian co-ordinates system, then
is any vector field in cartesian co-ordinates system, then
If S is any closed surface enclosing a volume V and 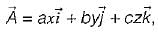 then the value of
then the value of 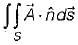 (
(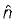 is a unit vector) will be equal to
is a unit vector) will be equal to
Assertion (A): The laplacian operator of a scalar function ϕ can be defined as “Gradient of the divergence of the scalar ϕ”
Reason (R): Laplacian operator may be a “scalar laplacian" or a “vector laplacian'’ depending upon whether it is operated with a scalar function or a vector, respectively.
Match List-I (Terms) with List-II (Type) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
A. Curl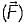 = 0
= 0
B. Div 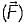 = 0
= 0
C. Div grad (ϕ) = 0
D. Div div (ϕ) = 0
List-ll
1. Laplace equation
2. Irrotational
3. Solenoidal
4. Not defined
Codes:
A B C D
(a) 2 3 1 4
(b) 4 1 3 2
(c) 2 1 3 4
(d) 4 3 1 2
If uF = ∇v, where u and v are scalar fields and F is a vector field, then F. curl F is equal to
A vector field which has a vanishing divergence is called as ____________
Which of the following statements is not true of a phasor?
Match List-I (Physical quantities) with List-ll (Dimensions) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
A. Electric potential
B. Magnetic flux
C. Magnetic field intensity
D. Magnetic flux density
List-ll
1. MT-2I-1
2. ML2T-3I-1
3. IL-1
4. ML2T-2I-1
Codes:
A B C D
(a) 2 4 3 1
(b) 4 2 3 1
(c) 1 2 1 3
(d) 4 2 1 3
Which of the following statements is not true regarding vector algebra?
A rigid body is rotating with an angular velocity of ω where, 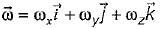 and v is the line velocity. If
and v is the line velocity. If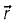 is the position vector given by
is the position vector given by  then the value of curl
then the value of curl 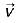 will be equal to
will be equal to


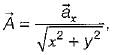 then the value of
then the value of 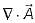 at (2, 2, 0) will be
at (2, 2, 0) will be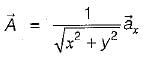
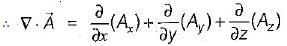
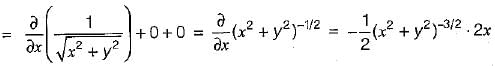
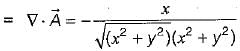
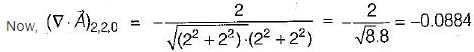
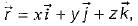 then the value of
then the value of 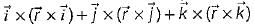 is
is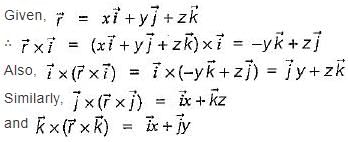
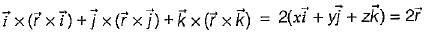

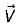 is solenoidal, therefore
is solenoidal, therefore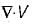 = 0
= 0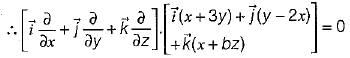
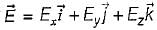 be any vector field in cartesian co-ordinate system then, we can prove that
be any vector field in cartesian co-ordinate system then, we can prove that 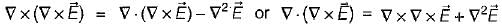
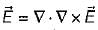
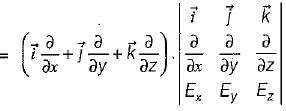
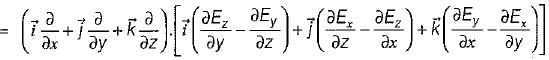
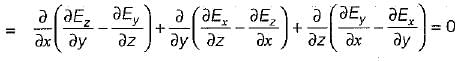
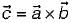 and
and 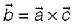 , then
, then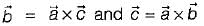
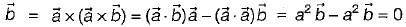
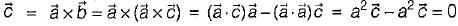
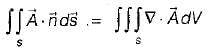
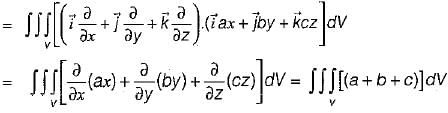
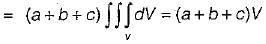
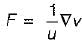
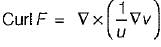
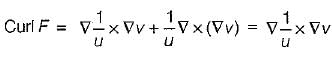
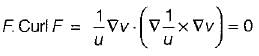
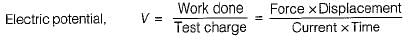
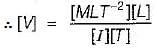
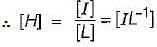
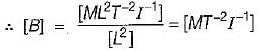
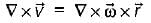
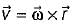 )
)
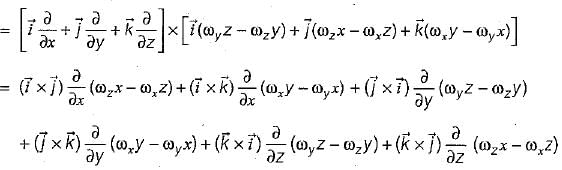
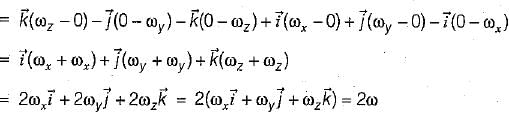
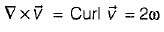
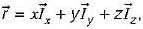 then which of the following relation will hold true?
then which of the following relation will hold true?