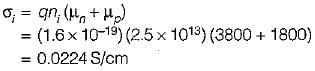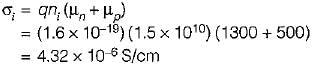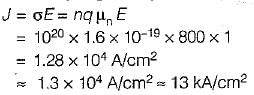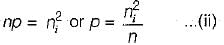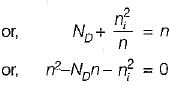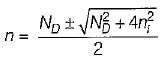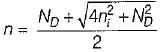Test: Semiconductor Physics - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test GATE Electrical Engineering (EE) Mock Test Series 2026 - Test: Semiconductor Physics
The mobility of free electrons and holes in pure germanium are 3800 and 1800 cm2/V-s respectively. The corresponding values for pure silicon are 1300 and 500 cm2/V-s, respectively. Assuming ni = 2.5 x 1013 cm-3 for germanium and ni = 1.5 x 1010 cm-3 for silicon at room temperature, the values of intrinsic conductivity for germanium and silicon are respectively given by
Assertion (A): In an n-type semiconductor, the majority carriers are electrons due to the addition of donor impurities.
Reason (R): Donor impurities introduce additional energy levels just below the conduction band, facilitating electron excitation.
Reason (R): Donor impurities introduce additional energy levels just below the conduction band, facilitating electron excitation.
When an electric field is applied across a semiconductor, free electrons in it will accelerate due to the applied field, and gain energy. This energy can be lost as heat when the electrons
Match the charge transport mechanism in List-I with its description in List-II:
List-I
A) Drift
B) Diffusion
C) Recombination
List-II
1. Movement of carriers due to a concentration gradient.
2. Net motion of carriers under an electric field.
3. Process where electrons and holes annihilate each other.
How does the bandgap of a material influence its suitability for use in high-frequency electronic devices?
If elements in column IV of the periodic table are placed in increasing order of their atomic number, the order will be
Assertion (A): The drift velocity is in the direction opposite to that of the electric field.
Reason (R): At each inelastic collision with an ion, an electron loses energy, and a steady-state condition is reached where a finite value of drift speed is attained.
The density and mobility of electrons in a conductor are respectively 1020/cm3 and 800 cm2/V-s. If a uniform electric field of 1 V/cm exists across this conductor, then the electron current density would be approximately
A semiconductor is doped with a donor density ND and no acceptors. If the intrinsic concentration is ni then the free electron density(n) will be equal to
Which of the following statements is TRUE about the effect of doping on the electrical properties of a semiconductor material?
|
26 docs|257 tests
|
|
26 docs|257 tests
|