Test: Aromaticity - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - Test: Aromaticity
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of polarity
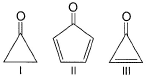
In principle, what is true regarding benzene and 1, 3, 5-cyclohexatriene?
Enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is -119 kJ/mol and that of benzene is -208 kJ/mol. Based on these information, resonance energy of benzene can be calculated to be
The following compound , when treated with excess of AgBF4 gives a red precipitate leaving a highly conducting filtrate, due to
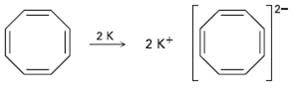
When potassium metal is added to 1, 3, 5, 7-cyclooctatetraene, a highly conducting salt is formed without evolution of H2 gas because
Direction (Q. Nos. 9 - 12) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
When considering electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions the halides are described as
Direction (Q. Nos. 13 - 17) This section is based on Statement i and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Q.
Statement I : Benzene has very high stability than a general triene.
Statement II : Benzene is a completely conjugated system.
Statement I: Pyrene, although aromatic, decolorises brown colour of bromine water.
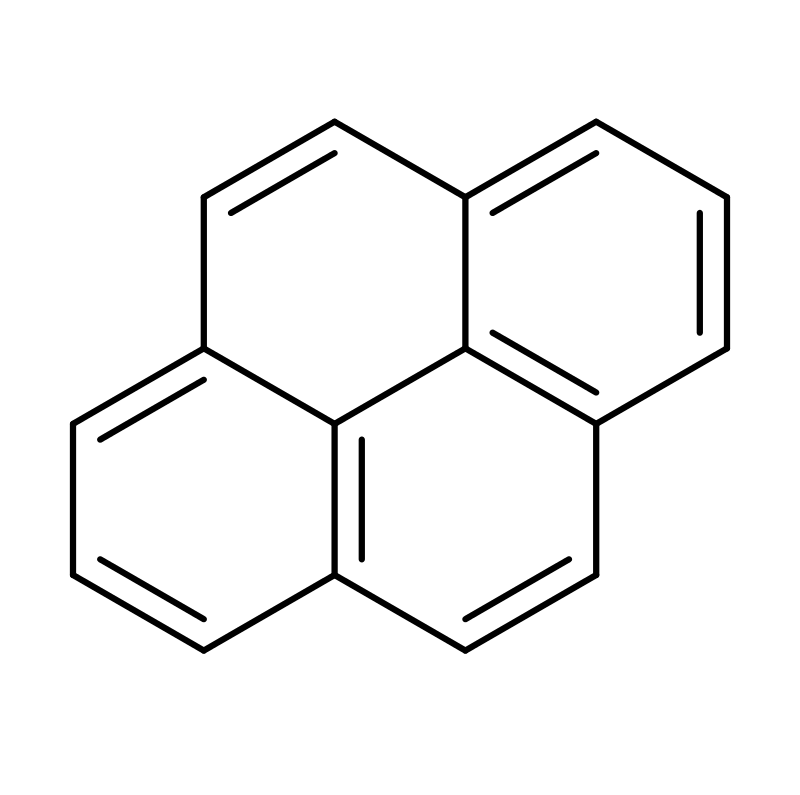
Statement II: It has one pi-bond extra which is not part of the aromatic system.
Statement I : The follow compound is optically active.
Statement II : It has a chiral carbon.
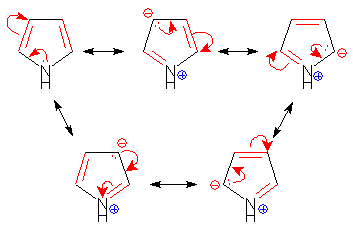
Statement I : Furan is an aromatic system, has resonance energy comparable to that of benzene.
Statement II : Furan decolourises the brown colour of bromine water solution.
Arrange the halogens F2, Cl2, Br2, I2 in order of their increasing reactivity with alkanes.
Direction (Q. Nos. 18 - 20) This section contains 3 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
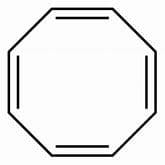
Cyclobutene when refluxed in presence of potassium metal, evolve hydrogen gas and an aromatic system is formed. How many pi-electrons are involved in the above formed aromatic system?
When two or more different substituents are attached with a benzene ring the number 1 position in the ring is given to a high priority group. Which one of the following groups has the highest - priority?
The compound below has four phenyl rings, but very less stable due to an opposing factor of stability. Therefore, this compound absorb bromine in dark.
How many bromine molecules, when added to this molecule, would make it stable and prevent further bromine addition?
[IIT JEE 2005]
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|