UPPSC GS I Practice Test - 10 (Old Pattern) - UPPSC (UP) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UPPSC Mock Test Series 2026 - UPPSC GS I Practice Test - 10 (Old Pattern)
The Lahore session of the Indian National Congress is significant because:
With reference to modern Indian history, Individual Satyagraha launched during the 1940s because
Which of the following is not a part of Cripps Proposal?
Consider the following statements regarding the Indian National Movement
1. Rajagopalachari formula of 1944 aimed to cons, hence the formation of states on a linguistic basis.
2.This formula was opposed by Mahatma Gandhi
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
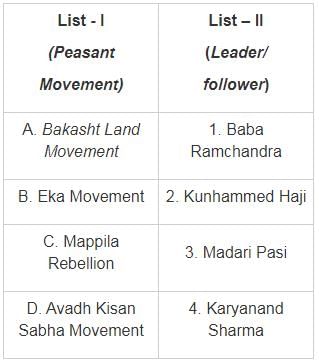
Match List - I with List-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below the lists:
With reference to the Eka movement, consider the following statements.
1. It was a peasant movement.
2. The main grievances were the extraction of high rent and the oppressionCongress’sdars.
3. The movement did not have a leadership of its own and remained under Congress’s leadership.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. James Augustus Hickey, in 1780, started the newspaper Bombay Samachar.
2. The Lahore Chronicle was started by Syed Muhammad Azim.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
In which of the following years did Sarojini Naidu preside over the Indian National Congress session?
Who was the last Nizam ruler of the erstwhile Hyderabad state?
The theory of Isostasy was developed by:
Asteroids are found between the orbits of:
Consider the following pairs:
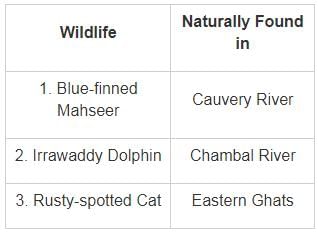
Which of the pairs above are correctly matched?
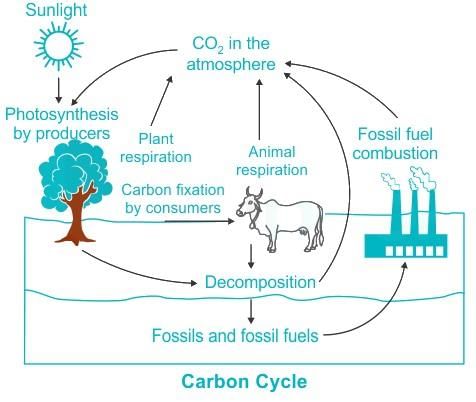
Which step is not involved in the carbon cycle?
Which one of the following factors is NOT connected with the planetary wind system?
Which one of the following is NOT a current of the Pacific Ocean?
Which type of land does alluvial sediment mean?
Shifting agriculture in Brazil is known as:
Assertion (A): Special Economic Zones are meant for attracting foreign companies.
Reason (R): Special Economic Zones provide more employment opportunities to the local people
What are the factors influencing the distribution of the population?
(1) Availability of water and climate
(2) Urbanization and industrialization
(3) Mineral resources
(4) Social factors
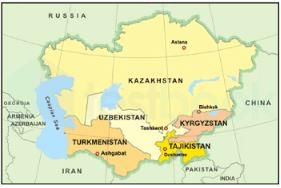
Which of the following Central Asian countries does NOT share its border with China?
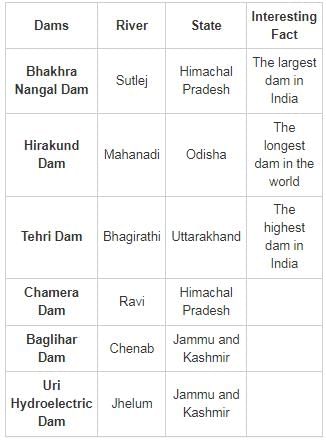
The Bhakra Nangal Dam is built across the River
Chilka Lake is a
(FreshwaterFreshwaterr lake
Which of the following are possible causes for monsoon delay in India
1. El Nino
2. Cyclonic Formation
3. Westerly Disturbances
4. Madden Julian Oscillation
Which of the factors given above is/are correct?
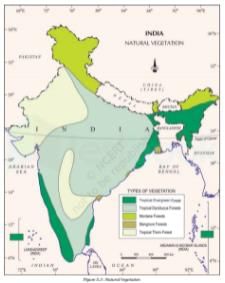
Trees like ebony, mahogany, rosewood, rubber, and cinchona are found in which type of forest?
With reference to the gold mines in India, which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. Gold reserves are highly scarce in India.
2. Some gold mines in India are very deep, which makes commercial extraction expensive.
Which of the following areas is the original habitat of the 'Toda tribe'?
Which state in India has the lowest population?
|
2 docs|37 tests
|