Important Questions: Reproduction in Animals - Class 8 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Important Questions: Reproduction in Animals
Which of the following statements is true about asexual reproduction?
Which of the following is/are paired structure in human reproductive system?
Which of the following statements about the human female egg cell is incorrect?
Which of the following sequences is in the correct order?
What develops into a new individual in animals during reproduction?
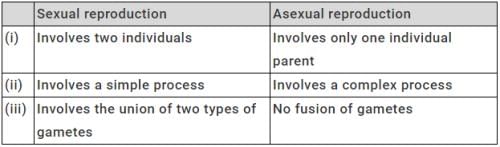
Which of the following comparisons are true of sexual and asexual reproduction?
The animals that produce new young ones are called
Which of the following shows external fertilisation?
Read the given information and identify P, Q and R.
P - An ovum is discharged by the ovary
Q - An embryo is Implanted in the uterus
R - The fusion of male and female gametes takes place
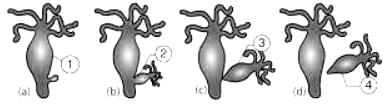
In Hydra, the mode of reproduction is