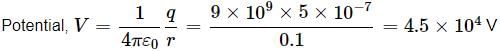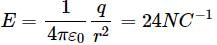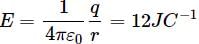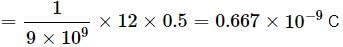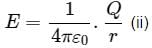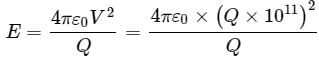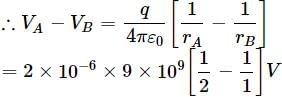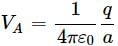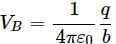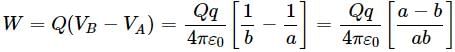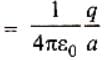Test: Electrostatic Potential & Potential due to a Point Charge (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions - Test: Electrostatic Potential & Potential due to a Point Charge (NCERT)
Which of the following statement is not true?
1 volt is equivalent to
The work done in bringing a unit positive charge from infinite distance to a point at distance x from a positive charge Q is W. Then the potential ϕ at that point is
The potential at a point due to a charge of 5×10−7C located 10cm10cm away is
In the question number 4, work done in bringing a charge of 4 x 10-9 C from infinity to that point is
The electric field intensity at a point P due to point charge q kept at point Q is 24 N C−1 and the electric potential at point P due to same charge is 12 J C−1. The order of magnitude of charge q is
The electric potential at a point in free space due to charge Q coulomb is Q x 1011 volts. The electric field at that point is
Two points A and B are located in diametrically opposite directions of a point charge of +2μC at distances 2m and 1m respectively from it. The potential difference between A and B is
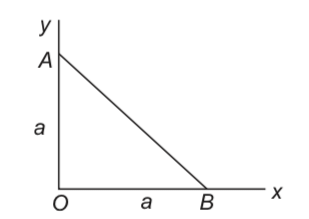
A charge +q is placed at the origin O of x-y axes as shown in the figure. The work done in taking a charge Q from A to B along the straight line AB is
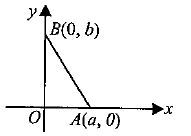
As per this diagram a point charge +q is placed at the origin O. Work done in taking another point charge −Q from the point A [coordinates (0, a)] to another point B [coordinates (a, 0)] along the straight path AB is
|
257 docs|234 tests
|