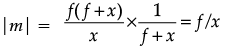Assertion & Reason Test: Ray Optics & Optical Instruments - 1 - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Assertion & Reason Test: Ray Optics & Optical Instruments - 1
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): The focal length of a concave mirror is f and an object is placed at a distance x from the focus. The magnification produced by the mirror is f/x.
Reason (R): magnification = size of image / size of object
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Air bubbles shine in water.
Reason (R): Air bubbles shine in water due to refraction of light.
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): A double convex air bubble is formed within a glass slab. The air bubble behaves like a converging lens.
Reason (R): Refractive index of glass is more than the refractive index of air.
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): A convex lens of focal length 30 cm can’t be used as a simple microscope in normal setting.
Reason (R): For normal setting, the angular magnification of simple microscope is M = D/f.
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Convex lens behaves like a simple microscope.
Reason (R): For larger magnifying power, the focal length of convex lens should be small.
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): A convex mirror cannot form real images.
Reason (R): Convex mirror converges the parallel rays that are incident on it.
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): The mirror formula 1/v + 1/u = 1/f is valid for mirrors of small aperture.
Reason (R): Laws of reflection of light is valid for only plane surface and not for large spherical surface.
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): A diamond of refractive index √6 is immersed in a liquid of refractive index √3 . If light travels from diamond to liquid, total internal reflection will take place when angle of incidence is 30°.
Reason (R): µ = 1/sin C, where µ is the refractive index of diamond with respect to the liquid
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): The scattering of light while passing through a true solution is called Tyndall effect.
Reason (R): Intensity of scattered light is inversely proportional to the fourth power of wavelength.
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): If the objective lens and the eyepiece lens of a microscope are interchanged, it works as a telescope.
Reason (R): Objective lens of telescope require large focal length and eyepiece lens require small focal length.
|
9 docs|1259 tests
|