Test: NEET Previous Year Questions: Work, Energy & Power - 2 - NEET MCQ
9 Questions MCQ Test - Test: NEET Previous Year Questions: Work, Energy & Power - 2
An ideal spring with spring-constant k is hung from the ceiling and a block of mass M is attached to its lower end. The mass is released with the spring initially unstretched. Then the maximum extension in the spring is
A spherical ball of mass m is kept at the highest point in the space between two fixed, concentric spheres A and B (see figure.) The smaller sphere A has a radius R and the space between the two spheres has a width d. The ball has a diameter very slightly less than d. All surfaces are frictionless. The ball is given a gentle push (towards the right in the figure). The angle made by the radius vector of the ball with the upward vertical is denoted by q (shown in the figure) [JEE-2002]
(a) Express the total normal reaction force exerted by the spheres on the ball as a function of angle q.
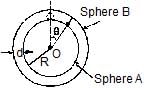
(b) Let NA and NB denote the magnitudes of the normal reaction force on the ball exerted by the spheres A and B, respectively. Sketch the variations of NA and NB as functions of cosq in the range 0 £ q £ p by drawing two separate graphs in your answer book, taking cosq on the horizontal axes.
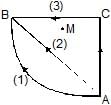
In a region of only gravitational field of mass `M' a particle is shifted from A to B via three different paths in the figure. The work done in different paths are W1, W2, W3 respectively then
[JEE(Scr.)-2003]
A particle is placed at the origin and a force F = kx is acting on it (where k is a positive constant). If U(0) = 0, the graph of U(x) versus x will be (where U is the potential energy function)
[JEE(Scr.)-2004]
A bob of mass M is suspended by a massless string of length L. The horizontal velocity V at position A is just sufficient to make it reach the point B. The angle q at which the speed of the bob is half of that at A, satisfies
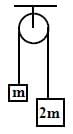
A light inextensible string that goes over a smooth fixed pulley as shown in the figure connects two blocks of masses 0.36 kg and 0.72 kg. Taking g = 10 m/s2, find the work done (in joules) by the string on the block of mass 0.36 kg during the first second after the system is released from rest.
A ball of mass (m) 0.5 kg is attached to the end of a string having length (L) 0.5 m. The ball is rotated on a horizontal circular path about vertical axis. The maximum tension that the string can bear is 324 N. the maximum possible value of angular velocity of ball (in radian/s) is
[jee-2011]
A block of mass 0.18 kg is attached to a spring of force-constant 2 N/m. The coefficient of friction between the block and the floor is 0.1. Initially the block is at rest and the spring is un-stretched. An impulse is given to the block as shown in the figure. The block slides a distance of 0.06 m and comes to rest for the first time. The initial velocity of the block in m/s is V = N/10. Then N is
[JEE-2011]
Two identical discs of same radius R are rotating about their axes in opposite directions with the same constant angular speed w. The discs are in the same horizontal plane At time t = 0, the points P and Q are facing each other as shown in the figure. The relative speed between the two points P and Q is nr.In one time period (T) of rotation of the discs, nr as a function of time is best represented by
[JEE-2012]



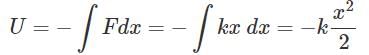 This is the equation of parabola symmetric to U axis in negative direction.
This is the equation of parabola symmetric to U axis in negative direction.