Test: Fertilisation and Implantation (November 4) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Daily Test for NEET Preparation - Test: Fertilisation and Implantation (November 4)
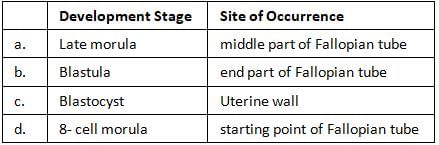
Identify the human development stage shown below as well as the related right place of its occurrence in a normal pregnant woman and select the right option for the two, together



Given below are four statements (i)-(iv) regarding embryonic development in humans.
(i) Cleavage divisions bring about considerable increase in the mass of protoplasm.
(ii) With more cleavage divisions, the resultant blastomeres become smaller and smaller.
(iii) The blastomeres in the blastocyst are arranged into two layers, trophoblast and endometrium.
(iv) Cleavage divisions result in a solid ball of cells called morula.
Which of the above two statements are correct?
(i) Cleavage divisions bring about considerable increase in the mass of protoplasm.
(ii) With more cleavage divisions, the resultant blastomeres become smaller and smaller.
(iii) The blastomeres in the blastocyst are arranged into two layers, trophoblast and endometrium.
(iv) Cleavage divisions result in a solid ball of cells called morula.
Which of the above two statements are correct?
In human adult females, oxytocin
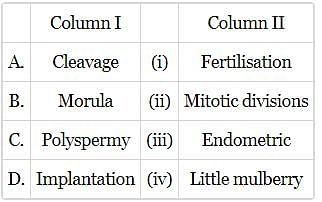
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the codes given.
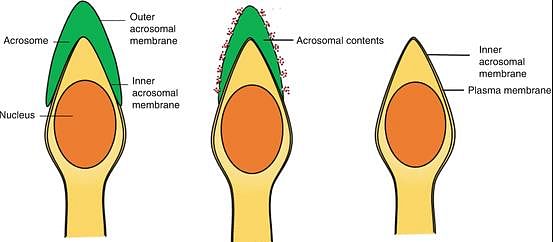
The sperms undergo physiological maturation, acquiring increased motility and fertilizing capacity in?
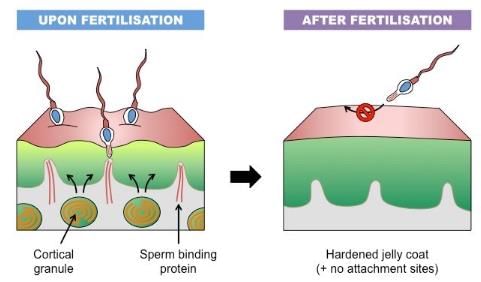
A reaction of granules content which hardens the zona pellucida and ensures sure block to polyspermy is ______________.
Fill up the blanks in the following paragraph by selecting the correct option.
During copulation (coitus), semen is released by the penis into the vagina and is called (i) . The ovum released by the ovary is transported to the (ii) where (iii) takes place. During fertilisation, a sperm comes in contact with the zona pellucida layer of the ovum and induces changes in the membrane that block the entry of (iv) . The secretions of the (v) help the sperm enter into the cytoplasm of the ovum.

Preparation of sperm before penetration of ovum is
Implantation takes place after __________ of fertilisation.
Besides activating the egg, another role of a sperm is to carry __________.
|
12 docs|366 tests
|