Test: Physical Properties & General Reaction (February 11) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Daily Test for NEET Preparation - Test: Physical Properties & General Reaction (February 11)
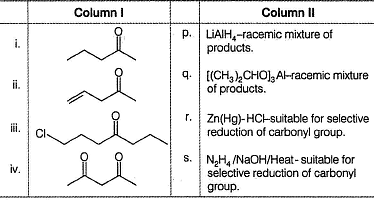
Match the reactants from Column I with the reagents and expected outcomes from Column II. Mark the correct option form the codes given below.

Which of the following will give a racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4 followed by acid work-up?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Consider the following reaction,
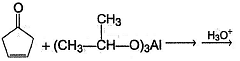
Q.
The organic product(s) formed above is/are
The reagent which can best bring about the following transformation is
If glyoxal glycol is treated with a mixture of CH3MgBr and C2H5MgBr in diethyl ether followed by acid hydrolysis, how many different diols would be formed, which are simultaneously optically active?
Which is the most suitable reagent for the following transformation?
One integer Value Correct Type
If all the aldehyde isomers of C5H10O is independently treated with HCN/NaCN solution, how many of them will give racemic mixture of cyanohydrin?
If one molecule of trioxane is heated, how many molecules of formaldehyde would be formed?
Consider the following reaction,
Q.
The correct deduction(s) regarding mechanism of the above reaction is/are
Consider the reaction given below,
Q.
X is formed in which a new ring is formed. How many atoms are present in this new ring?
|
12 docs|366 tests
|




















