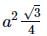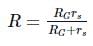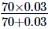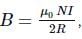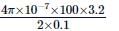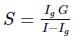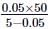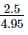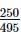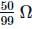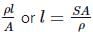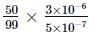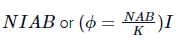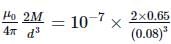Test: Torque on Current Loop Magnetic Dipole (December 30) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Daily Test for NEET Preparation - Test: Torque on Current Loop Magnetic Dipole (December 30)
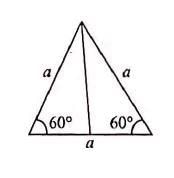
A uniform conducting wire of length length 10a and resistance R is wound up into four turn as a current carrying coil in the shape of equilateral triangle of side a. If current I is flowing through the coil then the magnetic moment of the coil is

A moving coil galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter by:
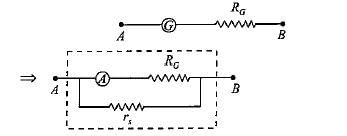
A galvanometer of resistance 70Ω, is converted to an ammeter by a shunt resistance rs = 0.03Ω. The value of its resistance will become
A circular coil of radius 10cm having 100 turns carries a current of 3.2A. The magnetic field at the center of the coil is
A galvanometer having a resistance of 50Ω, gives a full scale deflection for a current of 0.05A. The length (in metres) of a resistance wire of area of cross section 3 × 10−2cm2 that can be used to convert the galvanometer into an ammeter which can read a maximum of 5A current is
(Specific resistance of the wire ρ = 5 × 10−7Ωm)
A circular coil of 70 turns and radius 5 cm carrying a current of 8 A is suspended vertically in a uniform horizontal magnetic field of magnitude 1.5 T. The field lines make an angle of 30o with the normal of the coil then the magnitude of the counter torque that must be applied to prevent the coil from turning is
A galvanometer of resistance 10Ω gives full-scale deflection when 1mA current passes through it. The resistance required to convert it into a voltmeter reading upto 2.5V is
In a moving coil galvanometer the deflection (ϕ) on the scale by a pointer attached to the spring is
A short bar magnet has a magnetic moment of 0.65JT−1, then the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field produced by the magnet at a distance 8cm from the centre of magnet on the axis is
The torque on a current-carrying rectangular loop is τ when it is placed in a uniform magnetic field at an angle θ. If the length and the width of the loop is doubled then the torque on the loop at an angle θ will be:"
|
12 docs|366 tests
|