Test: Alkynes & Aromatic hydrocarbon (October 3) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Alkynes & Aromatic hydrocarbon (October 3)
What two atomic or hybrid orbitals overlap to form the carbon-carbon σ (sigma) bond in ethyne?
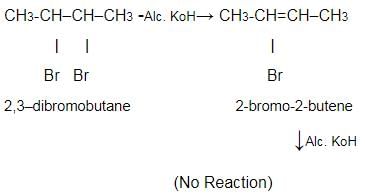
When 2,3-dibromobutane is treated with KOH in ethanol, 2-bromo-2-butene is formed which does not undergo further dehydrobromination to form 2-butyne under similar condition because
Which of the following reagents produces effervescence due to hydrogen gas (H₂) evolution when it reacts with 1-butyne (CH₃CH₂C≡CH) in an inert solvent?
Statement I : Treatment of either 1,2-dibromobutane or 2,2-dibromobutane with NaNH2 gives the same 1-butyne.
Statement II : NaNH2 forms salt with terminal alkyne which makes possible the above observation.
Statement l : C6H5MgBr with propyne gives 1-phenyl propyne.
Statement II : C6H5- is a very strong nucleophile.
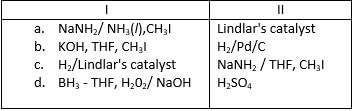
Which set of reagent(s) in correct order would accomplish the following transformation?
What is true about the final major product of the reaction?
Which of the following sets of reagent when applied sequentially, on 2-butyne will produce a meso product?
Direction (Q. Nos. 15 - 20) This section contains 2 paragraphs, each describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Six questions related to the paragraphs have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage I
Unlike alkenes, alkynes undergo nucleophilic addition as well as electrophilic addition as :
Q. Which of the following best describes what happens in the first step in the mechanism of reaction shown below?
Direction (Q. Nos. 21 - 24) This section contains 4 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. How many different isomeric alkynes on catalytic hydrogenation can give 2, 3, 4 -trimethyl heptane?