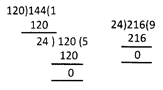Olympiad Test: Playing With Numbers - Class 6 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Online MCQ Tests for Class 6 - Olympiad Test: Playing With Numbers
What are the numbers which have more than two factors called?
What are the numbers which have only two factors (1 and the number itself) called?
Which is the number that is neither prime nor composite?
Which of the following is the L.C.M. of 36 and 72?
Which of the following is an example of an even number?
What do you get when you multiply two factors?
Every number is a _____ and a _____ of itself.
What are the numbers which are multiples of 2 called?
What is the H.C.F. of the two numbers equal to?
Which of these numbers is a factor of every number?
How many prime numbers are there between 1 and 50?
A is the 5th prime number. B is the 7th prime number. What is B - A?
What is the number of prime numbers between 50 and 60?
Which of the following is the prime factorisation of 140?
|
266 tests
|