Biology: CUET Mock Test - 2 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 - Biology: CUET Mock Test - 2
Arrange the following events of human embryo development in a correct sequence:
(A) Blastocyst formation
(B) Implantation
(C) Formation of morula
(D) Cleavage in zygote
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
What will be the number of genotypes and phenotypes obtained in F2 generation when male parent RRyy is crossed with female parent rrYY?
Which one of the following will represent low stability and high resilience?
When environmental conditions are favorable, then the population growth curve will be
Which of the following statements are correct?
(A) The male gamete in plants is produced in the ovary.
(B) Pollination can be carried out by wind, water, or animals.
(C) The style connects the stigma to the ovary.
(D) Self-pollination results in cross-breeding of different plant species.
(E) The process of fertilization creates a diploid zygote.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following statements are correct?
(A) Human reproduction is asexual and occurs through binary fission.
(B) The male reproductive system produces sperm and transfers them to the female reproductive system.
(C) The testes are located inside the scrotum to maintain a temperature lower than the body temperature for sperm production.
(D) The female reproductive system produces eggs and provides a site for fertilization and development of the fetus.
(E) The human reproductive system operates under hormonal control, with significant involvement of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and gonads.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
What structure aids in the transfer of sperm to the ovule in flowering plants?
The fusion of male and female gametes results in the formation of ___________.
What is the function of exons in eukaryotic gene expression?
What would happen, if in a gene encoding a polypeptide of 50 amino acids, 25th codon (UAU) is mutated to UAA?
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
On Galapagos island, Darwin observed variation in beaks of birds (Darwin's finches) and he concluded:
Which of the following factors contribute to changes in gene and allele frequencies, leading to speciation?
1. Gene migration or gene flow
2. Genetic drift
3. Mutation
4. Genetic recombination
5. Natural selection
Which of the following statements regarding the disease typhoid is/are correct?
(i) Salmonella typhi are the pathogenic bacteria which enter human intestine through contaminated food and water and migrate to other organs through blood.
(ii) Sustained high fever (39∘C to 40∘C), weakness, stomach pain, constipation, headache and loss of appetite are some common symptoms of typhoid.
(iii) Typhoid vaccine is available as DPT vaccine.
(iv) Widal test is used for diagnosis of typhoid fever.
(v) The patient of this disease is not required to be treated with antibiotics.
i. Anti-retroviral drugs can completely cure HIV/AIDS.
ii. Anti-retroviral drugs help control the replication of the virus and prolong the life of the patient.
iii. There is no vaccine available for HIV prevention, but safe sex practices can reduce transmission.
iv. HIV treatment is only effective during the early stages of infection.
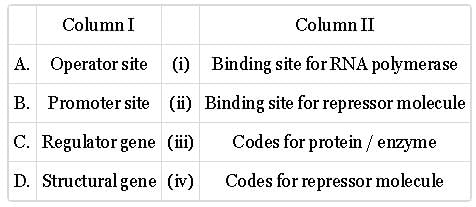
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from codes given below.

Which of the following reasons is mainly responsible for graft rejection in transplantation of organs? (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
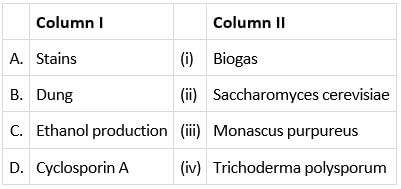
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the codes given below.
Which of the following statements regarding baculoviruses as biocontrol agents is/are correct?
The restriction enzyme responsible for the cleavage of following sequence is
5' - G - T - C - G - A - c - 3'
3' - C - A - G - C - T - G - 5'
Enzyme' Taq polymerase' used in PCR, has been isolated from bacterium ________.
Which of the following genes were introduced in cotton to protect it from cotton bollworms?
In an ecosystem if the Net Primary Productivity (NPP) of first trophic level is 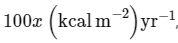 what would be the GPP (Gross Primary Productivity) of the third trophic level of the same ecosystem? (2024)
what would be the GPP (Gross Primary Productivity) of the third trophic level of the same ecosystem? (2024)
Which of the following statements regarding the diversity of plants and animals in tropical regions is/are correct?
i. Species diversity is generally higher in tropical regions compared to temperate and polar areas due to longer evolutionary timeframes.
ii. Tropical environments, being less seasonal and more constant, promote niche specialization which contributes to greater species diversity.
iii. The greater availability of solar energy in tropical regions leads to higher productivity, which indirectly supports greater biodiversity.
iv. Polar regions have been less affected by glaciation events than tropical regions, resulting in higher species diversity in the poles.
|
39 docs|145 tests
|



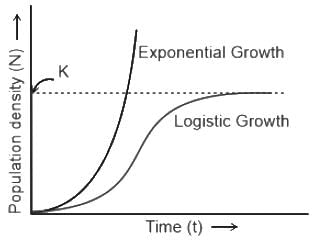
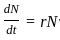
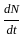 = Rate of change of population density.
= Rate of change of population density.