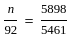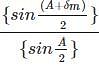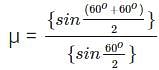Physics: CUET Mock Test - 3 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET Mock Test Series - Physics: CUET Mock Test - 3
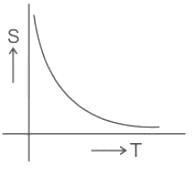
Which of the following graph correctly represents the variation of resistivity 's' with temperature 'T' for a semiconductor material ?
A proton and an alpha particle moving with same kinetic energy enter in the region of uniform magnetic field perpendicular to it. The ratio of radii of their trajectories will be:
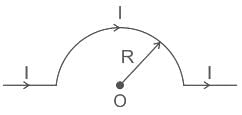
Magnetic field due to the current carrying wire as shown in the figure at point "O" will be:
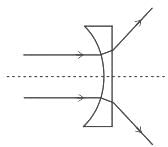
A plano-concave lens of focal length 10 cm is cut in to two equal parts then the power of each part is equal to_______ .
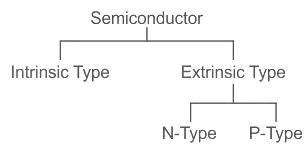
Which of the following is not an example of a semiconductor material?
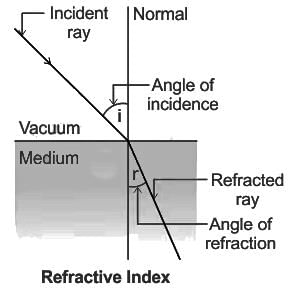
If the refractive index of water is 4/3 and that of glass is 5/3, then the critical angle of incidence for light tending to go from glass to water is:
Consider the following statements regarding electric dipole:
1. The SI unit for electric dipole moment is coulomb/meter
2. Its magnitude is equal to the product of the charge and the distance between the charges.
3. Its magnitude decreases with increasing distance between charges
Which of the above statement(s) is/are correct
Identify the expression for the motional electromotive force from the following?
What is the reactance of an inductor in a dc circuit?
How many types of power can be defined in an AC circuit?
Which among the following is true about transformers?
Identify the factor on which the angle of deviation of the prism does not depend.
A bar of length 0.7 m slides along metal rails at a speed of 1 m/s. The bar and rails are in a magnetic field of 20 T, pointing out into the page. Calculate the motional emf.
In which type of circuit the value of power factor will be minimum?
Which among the following varies in both magnitude and sign over a cycle?
Calculate the refractive index of the material of an equilateral prism for which the angle of minimum deviation is 60°.
A bar of length 0.15 m slides along metal rails at a speed of 5 m/s. The bar and rails are in a magnetic field of 40 T, pointing out into the page. The resistance of two resistors in parallel is both 20 Ω, and the resistance of the bar is 5 Ω. What is the current in the bar?
The frequency of ac is doubled. How does XL get affected?
Pick out the correct combination for a step-up transformer.
At what frequency will a coil, which has an inductance of 2.5 H, have a reactance of 3500 Ω?
What is the order of potential difference built up by the Van de Graff generator?
When was Van de Graff generator invented and by whom?
What happens to the frequency and the wavelength when light passes from a rarer to a denser medium?
|
8 docs|148 tests
|


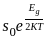

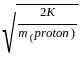
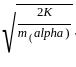
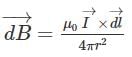
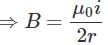
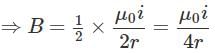
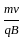
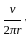
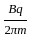
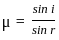
 --- (1)
--- (1)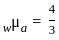
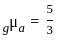
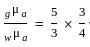
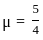
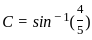
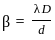
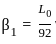
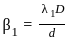
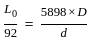 --- (1)
--- (1)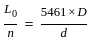 --- (2)
--- (2)